Escape from X inactivation varies in mouse tissues
- PMID: 25785854
- PMCID: PMC4364777
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005079
Escape from X inactivation varies in mouse tissues
Abstract
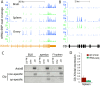
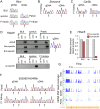
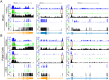
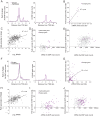
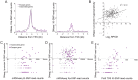
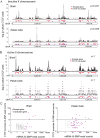
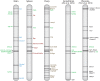
X chromosome inactivation (XCI) silences most genes on one X chromosome in female mammals, but some genes escape XCI. To identify escape genes in vivo and to explore molecular mechanisms that regulate this process we analyzed the allele-specific expression and chromatin structure of X-linked genes in mouse tissues and cells with skewed XCI and distinguishable alleles based on single nucleotide polymorphisms. Using a binomial model to assess allelic expression, we demonstrate a continuum between complete silencing and expression from the inactive X (Xi). The validity of the RNA-seq approach was verified using RT-PCR with species-specific primers or Sanger sequencing. Both common escape genes and genes with significant differences in XCI status between tissues were identified. Such genes may be candidates for tissue-specific sex differences. Overall, few genes (3-7%) escape XCI in any of the mouse tissues examined, suggesting stringent silencing and escape controls. In contrast, an in vitro system represented by the embryonic-kidney-derived Patski cell line showed a higher density of escape genes (21%), representing both kidney-specific escape genes and cell-line specific escape genes. Allele-specific RNA polymerase II occupancy and DNase I hypersensitivity at the promoter of genes on the Xi correlated well with levels of escape, consistent with an open chromatin structure at escape genes. Allele-specific CTCF binding on the Xi clustered at escape genes and was denser in brain compared to the Patski cell line, possibly contributing to a more compartmentalized structure of the Xi and fewer escape genes in brain compared to the cell line where larger domains of escape were observed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson CL, Brown CJ (2002) Variability of X chromosome inactivation: effect on levels of TIMP1 RNA and role of DNA methylation. Hum Genet 110: 271–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

