The TNF-family ligand TL1A and its receptor DR3 promote T cell-mediated allergic immunopathology by enhancing differentiation and pathogenicity of IL-9-producing T cells
- PMID: 25786692
- PMCID: PMC5112176
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401220
The TNF-family ligand TL1A and its receptor DR3 promote T cell-mediated allergic immunopathology by enhancing differentiation and pathogenicity of IL-9-producing T cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: The TNF-Family Ligand TL1A and Its Receptor DR3 Promote T Cell-Mediated Allergic Immunopathology by Enhancing Differentiation and Pathogenicity of IL-9-Producing T Cells.J Immunol. 2015 Dec 15;195(12):5839-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502026. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26637663 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
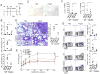
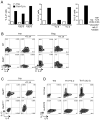
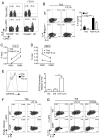
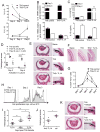
The TNF family cytokine TL1A (Tnfsf15) costimulates T cells and type 2 innate lymphocytes (ILC2) through its receptor DR3 (Tnfrsf25). DR3-deficient mice have reduced T cell accumulation at the site of inflammation and reduced ILC2-dependent immune responses in a number of models of autoimmune and allergic diseases. In allergic lung disease models, immunopathology and local Th2 and ILC2 accumulation is reduced in DR3-deficient mice despite normal systemic priming of Th2 responses and generation of T cells secreting IL-13 and IL-4, prompting the question of whether TL1A promotes the development of other T cell subsets that secrete cytokines to drive allergic disease. In this study, we find that TL1A potently promotes generation of murine T cells producing IL-9 (Th9) by signaling through DR3 in a cell-intrinsic manner. TL1A enhances Th9 differentiation through an IL-2 and STAT5-dependent mechanism, unlike the TNF-family member OX40, which promotes Th9 through IL-4 and STAT6. Th9 differentiated in the presence of TL1A are more pathogenic, and endogenous TL1A signaling through DR3 on T cells is required for maximal pathology and IL-9 production in allergic lung inflammation. Taken together, these data identify TL1A-DR3 interactions as a novel pathway that promotes Th9 differentiation and pathogenicity. TL1A may be a potential therapeutic target in diseases dependent on IL-9.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Buchan SL, Taraban VY, Slebioda TJ, James S, Cunningham AF, Al-Shamkhani A. Death receptor 3 is essential for generating optimal protective CD4(+) T-cell immunity against Salmonella. European journal of immunology. 2012;42:580–588. - PubMed
-
- Twohig JP, Marsden M, Cuff SM, Ferdinand JR, Gallimore AM, Perks WV, Al-Shamkhani A, Humphreys IR, Wang EC. The death receptor 3/TL1A pathway is essential for efficient development of antiviral CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell immunity. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2012;26:3575–3586. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cassatella MA, Pereira-da-Silva G, Tinazzi I, Facchetti F, Scapini P, Calzetti F, Tamassia N, Wei P, Nardelli B, Roschke V, Vecchi A, Mantovani A, Bambara LM, Edwards SW, Carletto A. Soluble TNF-like cytokine (TL1A) production by immune complexes stimulated monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of immunology. 2007;178:7325–7333. - PubMed
-
- Bamias G, Siakavellas SI, Stamatelopoulos KS, Chryssochoou E, Papamichael C, Sfikakis PP. Circulating levels of TNF-like cytokine 1A (TL1A) and its decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical immunology. 2008;129:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Bamias G, Martin C, 3rd, Marini M, Hoang S, Mishina M, Ross WG, Sachedina MA, Friel CM, Mize J, Bickston SJ, Pizarro TT, Wei P, Cominelli F. Expression, localization, and functional activity of TL1A, a novel Th1-polarizing cytokine in inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of immunology. 2003;171:4868–4874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

