Anthocyanins and their physiologically relevant metabolites alter the expression of IL-6 and VCAM-1 in CD40L and oxidized LDL challenged vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 25787755
- PMCID: PMC4950056
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201400803
Anthocyanins and their physiologically relevant metabolites alter the expression of IL-6 and VCAM-1 in CD40L and oxidized LDL challenged vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
Scope: In vitro and in vivo studies suggest that dietary anthocyanins modulate cardiovascular disease risk; however, given anthocyanins extensive metabolism, it is likely that their degradation products and conjugated metabolites are responsible for this reported bioactivity.
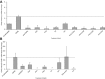
Methods and results: Human vascular endothelial cells were stimulated with either oxidized LDL (oxLDL) or cluster of differentiation 40 ligand (CD40L) and cotreated with cyanidin-3-glucoside and 11 of its recently identified metabolites, at 0.1, 1, and 10 μM concentrations. Protein and gene expression of IL-6 and VCAM-1 was quantified by ELISA and RT-qPCR. In oxLDL-stimulated cells the parent anthocyanin had no effect on IL-6 production, whereas numerous anthocyanin metabolites significantly reduced IL-6 protein levels; phase II conjugates of protocatechuic acid produced the greatest effects (>75% reduction, p ≤ 0.05). In CD40L-stimulated cells the anthocyanin and its phase II metabolites reduced IL-6 protein production, where protocatechuic acid-4-sulfate induced the greatest reduction (>96% reduction, p ≤ 0.03). Similarly, the anthocyanin and its metabolites reduced VCAM-1 protein production, with ferulic acid producing the greatest effect (>65% reduction, p ≤ 0.04).
Conclusion: These novel data provide evidence to suggest that anthocyanin metabolites are bioactive at physiologically relevant concentrations and have the potential to modulate cardiovascular disease progression by altering the expression of inflammatory mediators.
Keywords: Adhesion molecule; Cyanidin-3-glucoside; Cytokine; Inflammation; Metabolites.
© 2015 The Authors. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures





References
-
- Zhu, Y. , Xia, M. , Yang, Y. , Liu, F. et al., Purified anthocyanin supplementation improves endothelial function via NO‐cGMP activation in hypercholesterolemic individuals. Clin. Chem. 2011, 167361. - PubMed
-
- Edirisinghe, I. , Banaszewski, K. , Cappozzo, J. , McCarthy, D. , Burton‐Freeman, B. M. , Effect of black currant anthocyanins on the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in vitro in human endothelial cells. J. Agricult. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8616–8624. - PubMed
-
- Nizamutdinova, I. T. , Kim, Y. M. , Chung, J. I. , Shin, S. C. et al., Anthocyanins from black soybean seed coats preferentially inhibit TNF‐α‐mediated induction of VCAM‐1 over ICAM‐1 through the regulation of GATAs and IRF‐1. J. Agricult. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7324–7330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/H004963/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H532059/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- B/H004963/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I005943/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J004545/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

