Pyruvate kinase M2 prevents apoptosis via modulating Bim stability and associates with poor outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25788265
- PMCID: PMC4466635
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3262
Pyruvate kinase M2 prevents apoptosis via modulating Bim stability and associates with poor outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
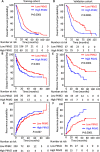
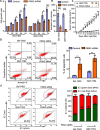
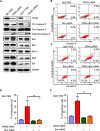
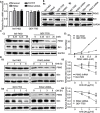
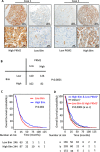
Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) contributes to the Warburg effect, a hallmark of cancer. We showed that PKM2 levels were correlated with overall survival (hazard ration = 1.675, 95% confidence interval: 1.389-2.019, P < 0.001) and disease-free survival (hazard ration = 1.573, 95% confidence interval: 1.214-2.038, P < 0.001) in a cohort of 490 patients with HCC. The correlations were further validated in an independent cohort of 148 HCC patients. Multivariate analyses revealed that PKM2 was an independent indicator of poor outcome in HCC. The knockdown of PKM2 in HCC cells inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Bim siRNA markedly abolished the PKM2-depletion-induced apoptosis. PKM2 depletion decreased the degradation of Bim. In clinical samples, PKM2 expression was reversely correlated with Bim expression. Combination of PKM2 and Bim levels had the best prognostic significance. We suggest that PKM2 serves as a promising biomarker for poor prognosis of patients with HCC and its knockdown induces HCC apoptosis by stabilizing Bim.
Keywords: Bim; PKM2; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Koppenol WH, Bounds PL, Dang CV. Otto Warburg's contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:325–337. - PubMed
-
- Yuan C, Li Z, Wang Y, Qi B, Zhang W, Ye J, Wu H, Jiang H, Song LN, Yang J, Cheng J. Overexpression of metabolic markers PKM2 and LDH5 correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features and adverse patient prognosis in tongue cancer. Histopathology. 2014;65:595–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

