Substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs
- PMID: 25788516
- PMCID: PMC4402958
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00072-14
Substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs
Abstract
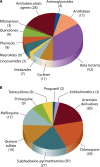
Substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs are a growing global problem. The most common substandard/counterfeit antimicrobials include beta-lactams (among antibiotics) and chloroquine and artemisin derivatives (among antimalarials). The most common type of substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs have a reduced amount of the active drug, and the majority of them are manufactured in Southeast Asia and Africa. Counterfeit antimicrobial drugs may cause increased mortality and morbidity and pose a danger to patients. Here we review the literature with regard to the issue of substandard/counterfeit antimicrobials and describe the prevalence of this problem, the different types of substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs, and the consequences for the individuals and global public health. Local, national, and international initiatives are required to combat this very important public health issue.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



References
-
- WHO. 1999. Counterfeit and sub-standard drugs in Myanmar and Vietnam. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Roy J. 1994. The menace of substandard drugs. World Health Forum 15:406–407. - PubMed

