The role of microRNA-1246 in the regulation of B cell activation and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 25789080
- PMCID: PMC4364674
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-015-0063-7
The role of microRNA-1246 in the regulation of B cell activation and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has not yet been completely elucidated. One of the hallmarks of SLE is the production of autoantibodies by uncontrolled over-activated B cells. Early B cell factor 1 (EBF1) contributes to the development, activation, and proliferation of B cells through activation of the AKT signaling pathway. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that several microRNAs (miRNAs) contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases through the regulation of B cells in SLE. We aim to investigate the expression patterns of miR-1246 in B cells and its contribution to pathogenesis of SLE.
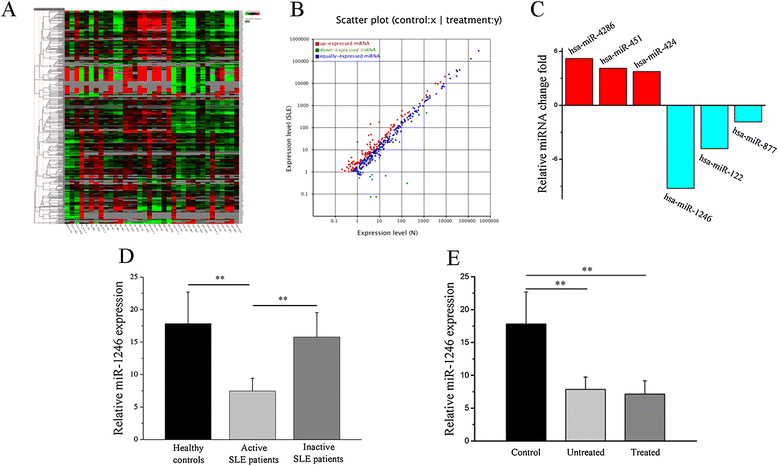
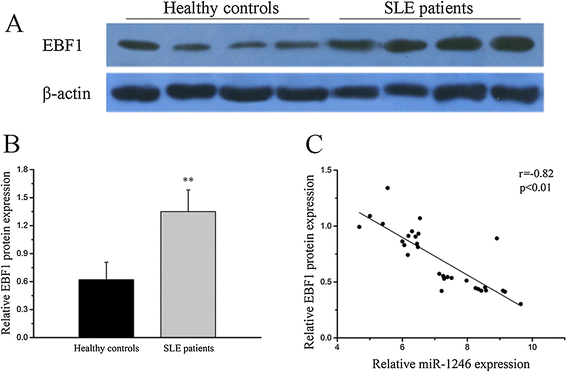
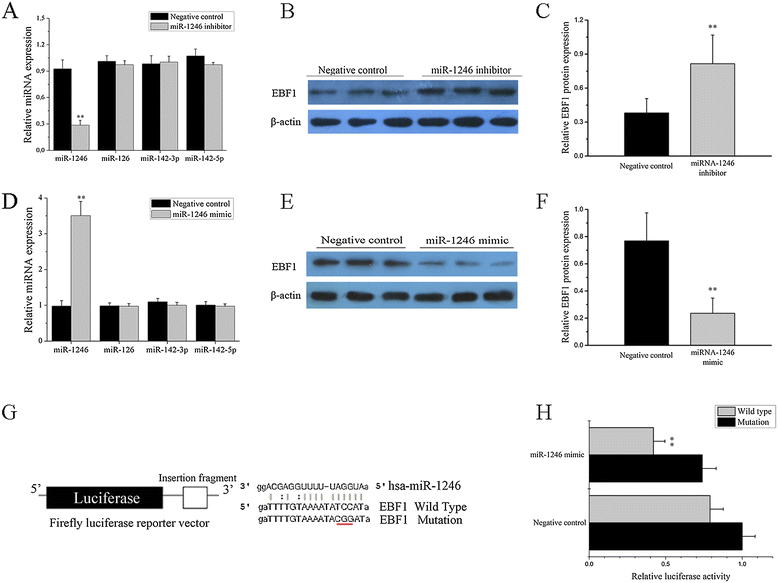
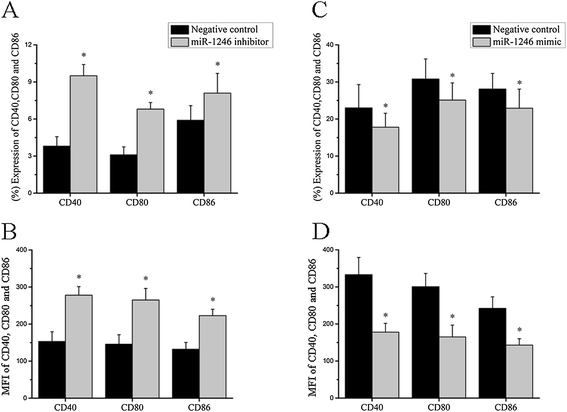
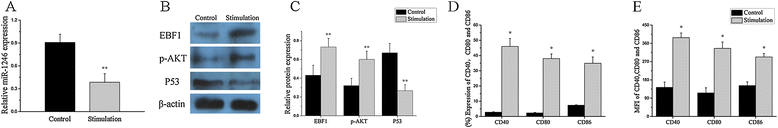
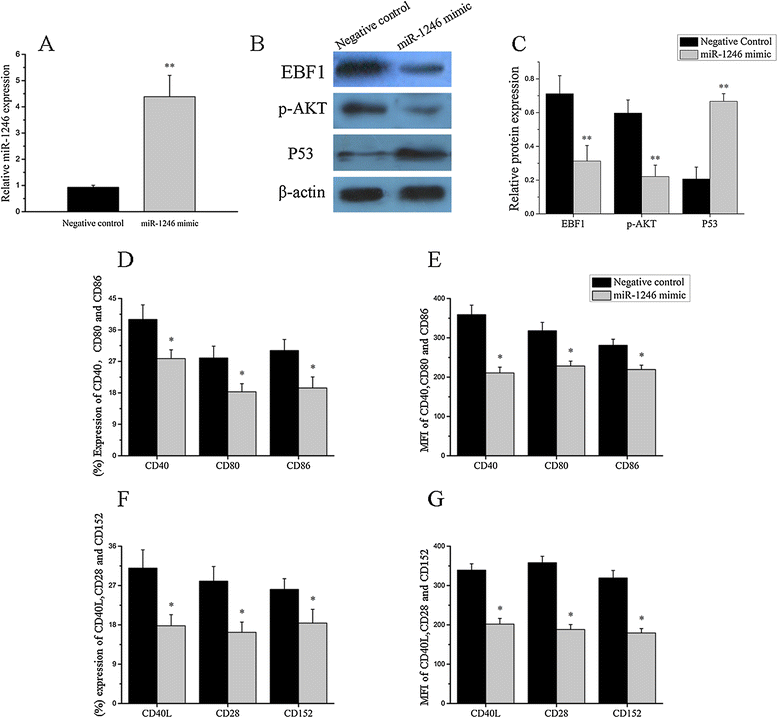
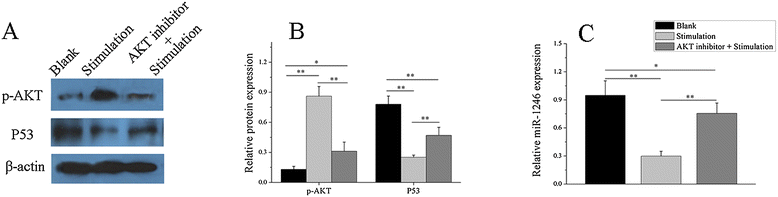
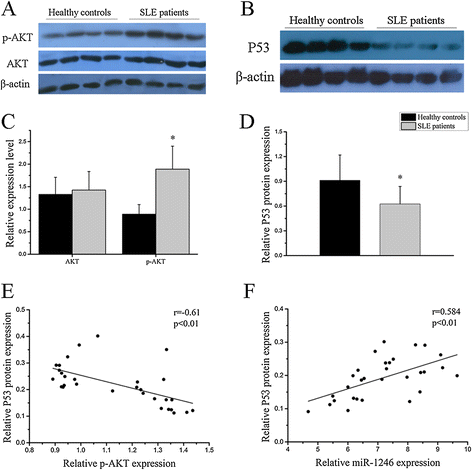
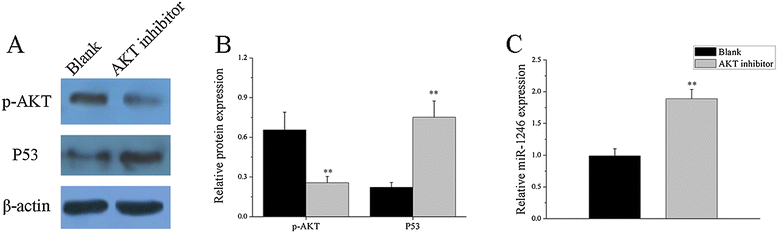
Results: Our results showed that the expression of miR-1246 was significantly decreased in B cells from SLE patients. We verified that miR-1246 specifically targeted the EBF1 messenger RNA (mRNA) by interacting with its 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) and regulated the expression of EBF1. Transfection of miR-1246 inhibitors into healthy B cells upregulated the expression of EBF1, enhanced B cell function, and increased the production of B cell surface co-stimulatory molecules CD40, CD80, and CD86. We also observed that abnormal activation of the AKT signaling pathway was associated with decreased P53 expression, leading to the downregulation of the miR-1246 expression; and upregulation of the miR-1246 expression reversed the responsiveness of B cells by inhibiting EBF1 expression.
Conclusions: Activated B cells in lupus could decrease the expression of miR-1246 through the AKT-P53 signaling pathway, which in turn enhances the expression of EBF1, thereby promoting further activation of B cells. Conversely, upregulation of miR-1246 could interrupt this amplification pathway. Our findings thus provide a theoretical framework towards the research of novel biological targets in SLE treatment.
Keywords: AKT; B cell; Co-stimulatory molecules; EBF1; Has-miR-1246; P53; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Defective PTEN regulation contributes to B cell hyperresponsiveness in systemic lupus erythematosus.Sci Transl Med. 2014 Jul 23;6(246):246ra99. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009131. Sci Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25101889
-
Decreased microRNA-142-3p/5p expression causes CD4+ T cell activation and B cell hyperstimulation in systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Sep;64(9):2953-63. doi: 10.1002/art.34505. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22549634
-
Aberrant T cell expression of Ca2+ influx-regulated miRNAs in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus promotes lupus pathogenesis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Feb;54(2):343-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu322. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25172935
-
SiLEncing SLE: the power and promise of small noncoding RNAs.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2008 Sep;20(5):526-31. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328304b45e. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18698172 Review.
-
The immunological basis of B-cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus.Int J Rheum Dis. 2010 Feb 1;13(1):3-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2009.01458.x. Int J Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 20374380 Review.
Cited by
-
Are Follicular Regulatory T Cells Involved in Autoimmune Diseases?Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 11;8:1790. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01790. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29312316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico identification of microRNAs predicted to regulate N-myristoyltransferase and Methionine Aminopeptidase 2 functions in cancer and infectious diseases.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 26;13(3):e0194612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194612. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29579063 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine-dependent modification of circGARS acts as a new player that promotes SLE progression through the NF-κB/A20 axis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Feb 4;24(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02732-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35120571 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression in Cutaneous Lupus: A New Window to Understand Its Pathogenesis.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Dec 30;2019:5049245. doi: 10.1155/2019/5049245. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 32082077 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of MicroRNAs in Modulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis.J Immunol Res. 2018 May 8;2018:4126106. doi: 10.1155/2018/4126106. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29854836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

