Examining the whole bowel, double balloon enteroscopy: Indications, diagnostic yield and complications
- PMID: 25789095
- PMCID: PMC4360443
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i3.247
Examining the whole bowel, double balloon enteroscopy: Indications, diagnostic yield and complications
Abstract
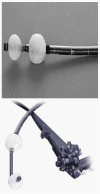
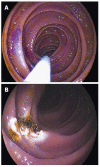
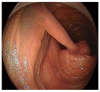
Double balloon enteroscopy (DBE) is an advanced type of endoscopic procedure which brings the advantage of reaching the whole small bowel using anterograde or the retrograde route. This procedure is both diagnostic and interventional for a variety of small intestinal diseases, such as vascular lesions, tumors, polyps and involvement of inflammatory bowel diseases. Main indication is the diagnosis and treatment of mid-gastrointestinal bleeding according to the recent published data all over the world. The complication rates seem to be higher than conventional procedures but growing experience is lowering them and improving the procedure to be safe and well tolerated. This review is about the technique, indications, diagnostic importance and complications of DBE according to the literature growing since 2001.
Keywords: Double balloon enteroscopy; Endoscopy; Small bowel.
Figures

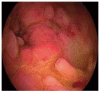
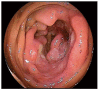
References
-
- Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Sato Y, Higashizawa T, Miyata T, Iino S, Ido K, Sugano K. Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:216–220. - PubMed
-
- Gerson LB, Flodin JT, Miyabayashi K. Balloon-assisted enteroscopy: technology and troubleshooting. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:1158–1167. - PubMed
-
- Choi H, Choi KY, Eun CS, Jang HJ, Park DI, Chang DK, Kim JO, Ko BM, Lee MS, Huh KC, et al. Korean experience with double balloon endoscopy: Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases multi-center study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:S22–S25. - PubMed
-
- Sun B, Rajan E, Cheng S, Shen R, Zhang C, Zhang S, Wu Y, Zhong J. Diagnostic yield and therapeutic impact of double-balloon enteroscopy in a large cohort of patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:2011–2015. - PubMed
-
- May A, Nachbar L, Ell C. Double-balloon enteroscopy (push-and-pull enteroscopy) of the small bowel: feasibility and diagnostic and therapeutic yield in patients with suspected small bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62:62–70. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

