Stranglehold on the spindle assembly checkpoint: the human papillomavirus E2 protein provokes BUBR1-dependent aneuploidy
- PMID: 25789401
- PMCID: PMC4614697
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1021519
Stranglehold on the spindle assembly checkpoint: the human papillomavirus E2 protein provokes BUBR1-dependent aneuploidy
Abstract
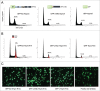
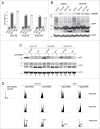
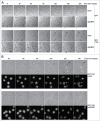
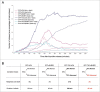
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) E2 protein, which inhibits the E6 and E7 viral oncogenes, is believed to have anti-oncogenic properties. Here, we challenge this view and show that HPV-18 E2 over-activates the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint (SAC) and induces DNA breaks in mitosis followed by aneuploidy. This phenotype is associated with interaction of E2 with the Mitotic Checkpoint Complex (MCC) proteins Cdc20, MAD2 and BUBR1. While BUBR1 silencing rescues the mitotic phenotype induced by E2, p53 silencing or presence of E6/E7 (inactivating p53 and increasing BUBR1 levels respectively) both amplify it. This work pinpoints E2 as a key protein in the initiation of HPV-induced cervical cancer and identifies the SAC as a target for oncogenic pathogens. Moreover, our results suggest a role of p53 in regulating the mitotic process itself and highlight SAC over-activation in a p53-negative context as a highly pathogenic event.
Keywords: APC/C, Anaphase Promoting Complex/Cyclosome; Ad, Adenovirus; BUBR1; E2; E2 TAD, E2 Transactivation Domain; E2 ΔTAD, E2 deleted of the Transactivation Domain; GFP, Green Fluorescent Protein; HPV, Human Papillomavirus; MCC, Mitotic Checkpoint Complex; MS, Mass Spectrometry; Noco, Nocodazole; SAC, Spindle Assembly Checkpoint; Thym, Thymidine; aneuploidy; m.o.i., Multiplicity of Infection; mitosis; p53; papillomavirus; spindle assembly checkpoint.
Figures


References
-
- zur Hausen H. Condylomata acuminata and human genital cancer. Cancer Res 1976; 36: 794; PMID:175942 - PubMed
-
- Schiffman M, Castle PE, Jeronimo J, Rodriguez AC, Wacholder S. Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Lancet 2007; 370: 890-907; PMID:17826171; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61416-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ, Howley PM. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990; 63: 1129-36; PMID:2175676; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Werness BA, Levine AJ, Howley PM. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science 1990; 248: 76-9; PMID:2157286; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.2157286 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scheffner M, Huibregtse JM, Vierstra RD, Howley PM. The HPV16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell 1993; 75: 495-505; PMID:8221889; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90384-3 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
