Identification of five driver gene mutations in patients with treatment-naïve lung adenocarcinoma in Taiwan
- PMID: 25789627
- PMCID: PMC4366385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120852
Identification of five driver gene mutations in patients with treatment-naïve lung adenocarcinoma in Taiwan
Abstract
Background: It is important to select appropriate targeted therapies for subgroups of patients with lung adenocarcinoma who have specific gene alterations.
Methods: This prospective study was a multicenter project conducted in Taiwan for assessment of lung adenocarcinoma genetic tests. Five oncogenic drivers, including EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, HER2 and EML4-ALK fusion mutations, were tested. EGFR, KRAS, BRAF and HER2 mutations were assessed by MALDI-TOF MS (Cohort 1). EML4-ALK translocation was tested by Ventana method in EGFR-wild type patients (Cohort 2).
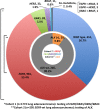
Results: From August 2011 to November 2013, a total of 1772 patients with lung adenocarcinoma were enrolled. In Cohort 1 analysis, EGFR, KRAS, HER2 and BRAF mutations were identified in 987 (55.7%), 93 (5.2%), 36 (2.0%) and 12 (0.7%) patients, respectively. Most of these mutations were mutually exclusive, except for co-mutations in seven patients (3 with EGFR + KRAS, 3 with EGFR + HER2 and 1 with KRAS + BRAF). In Cohort 2 analysis, 29 of 295 EGFR-wild type patients (9.8%) were positive for EML4-ALK translocation. EGFR mutations were more common in female patients and non-smokers and KRAS mutations were more common in male patients and smokers. Gender and smoking status were not correlated significantly with HER2, BRAF and EML4-ALK mutations. EML4-ALK translocation was more common in patients with younger age.
Conclusion: This was the first study in Taiwan to explore the incidence of five oncogenic drivers in patients with lung adenocarcinoma and the results could be valuable for physicians in consideration of targeted therapy and inclusion of clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous