Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system
- PMID: 25789684
- PMCID: PMC4507498
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3123
Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system
Abstract
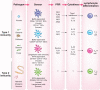
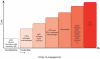
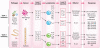
Microbial infections are recognized by the innate immune system both to elicit immediate defense and to generate long-lasting adaptive immunity. To detect and respond to vastly different groups of pathogens, the innate immune system uses several recognition systems that rely on sensing common structural and functional features associated with different classes of microorganisms. These recognition systems determine microbial location, viability, replication and pathogenicity. Detection of these features by recognition pathways of the innate immune system is translated into different classes of effector responses though specialized populations of dendritic cells. Multiple mechanisms for the induction of immune responses are variations on a common design principle wherein the cells that sense infections produce one set of cytokines to induce lymphocytes to produce another set of cytokines, which in turn activate effector responses. Here we discuss these emerging principles of innate control of adaptive immunity.
Figures
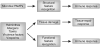

References
-
- Janeway CA., Jr. Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1989;54:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010;11:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Chen ZJ. Innate immune sensing and signaling of cytosolic nucleic acids. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014;32:461–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI089771/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI089771/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI064705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI064705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI054359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071754/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI081884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI081884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK071754/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

