Cell cycle, cytoskeleton dynamics and beyond: the many functions of cyclins and CDK inhibitors
- PMID: 25789852
- PMCID: PMC4614797
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2014.998085
Cell cycle, cytoskeleton dynamics and beyond: the many functions of cyclins and CDK inhibitors
Abstract
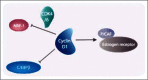
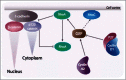
While targeting experiments carried out on the genes encoding many cell cycle regulators have challenged our views of cell cycle control, they also suggest that redundancy might not be the only explanation for the observed perplexing phenotypes. Indeed, several observations hint at functions of cyclins and CDK inhibitors that cannot be accounted for by their sole role as kinase regulators. They are found involved in many cellular transactions, depending or not on CDKs that are not directly linked to cell cycle control, but participating to general mechanisms such as transcription, DNA repair or cytoskeleton dynamics. In this review we discuss the roles that these alternative functions might have in cancer cell proliferation and migration that sometime even challenge their definition as proliferation markers.
Keywords: EMT; Rho GTPases; cytoskeleton; invasion; mitosis; transcription.
Figures




References
-
- Nigg EA. Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2:21-32; PMID:11413462; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35048096 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pines J. Four-dimensional control of the cell cycle. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1:E73-9; PMID:10559915; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/11041 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santamaria D, Barriere C, Cerqueira S, Hunt A, Tardy C, Newton K, Caceres JF, Dubus P, Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle. Nature 2007; 448:811-5; PMID:17700700; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature06046 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hochegger H, Takeda S, Hunt T. Cyclin-dependent kinases and cell-cycle transitions: does one fit all? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9:910-6; PMID:18813291; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm2510 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geng Y, Yu Q, Sicinska E, Das M, Schneider JE, Bhattacharya S, Rideout WM, Bronson RT, Gardner H, Sicinski P. Cyclin E ablation in the mouse. Cell 2003; 114:431-43; PMID:12941272; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00645-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
