IGFBP-rP1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 25789970
- PMCID: PMC4385937
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2015.59
IGFBP-rP1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
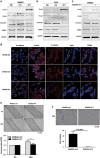
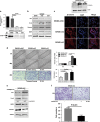
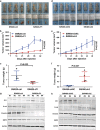
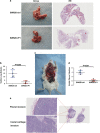
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) was initially recognized during organogenesis and has recently been reported to be involved in promoting cancer invasion and metastasis. Cooperation of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and other signaling pathways, such as Ras and Wnt, is essential to inducing EMT, but the molecular mechanisms remain to be fully determined. Here, we reported that insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1), a potential tumor suppressor, controls EMT in colorectal cancer progression. We revealed the inhibitory role of IGFBP-rP1 through analyses of clinical colorectal cancer samples and various EMT and metastasis models in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we demonstrated that IGFBP-rP1 suppresses EMT and tumor metastasis by repressing TGF-β-mediated EMT through the Smad signaling cascade. These data establish that IGFBP-rP1 functions as a suppressor of EMT and metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt activation play a critical role in the process of hepatocyte growth factor-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Int J Oncol. 2013 Feb;42(2):556-64. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1726. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23229794
-
Tumor suppressor gene insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) induces senescence-like growth arrest in colorectal cancer cells.Exp Mol Pathol. 2008 Oct;85(2):141-5. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2008.04.005. Epub 2008 May 11. Exp Mol Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18701096
-
MEGF6 Promotes the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via the TGFβ/SMAD Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(5):1895-1906. doi: 10.1159/000489374. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29719292
-
Regulatory miRNAs in Colorectal Carcinogenesis and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 22;18(4):890. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040890. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28441730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of TGF-β signaling in carcinogenesis and breast cancer metastasis.Breast Cancer. 2012 Apr;19(2):118-24. doi: 10.1007/s12282-011-0321-2. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Breast Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22139728 Review.
Cited by
-
Ornithine decarboxylase antizyme inhibitor 2 (AZIN2) is a signature of secretory phenotype and independent predictor of adverse prognosis in colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 15;14(2):e0211564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211564. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30768610 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through RAS signaling pathway and therapeutic implications in human cancer.J Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Sep;12(3):513-527. doi: 10.1007/s12079-017-0441-3. Epub 2018 Jan 12. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 29330773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NUBPL, a novel metastasis-related gene, promotes colorectal carcinoma cell motility by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Cancer Sci. 2017 Jun;108(6):1169-1176. doi: 10.1111/cas.13243. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28346728 Free PMC article.
-
The loss-of-function mutations and down-regulated expression of ASB3 gene promote the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells.Chin J Cancer. 2017 Jan 14;36(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0180-0. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28088228 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant over-expression of COX-1 intersects multiple pro-tumorigenic pathways in high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):21353-68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3860. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25972361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell GP, Thompson BJ. Colorectal cancer progression: lessons from Drosophila. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;28:70–77. - PubMed
-
- Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–695. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871–890. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH. Dissecting the metastatic cascade. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:448–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

