Long noncoding RNA lincRNA-p21 is the major mediator of UVB-induced and p53-dependent apoptosis in keratinocytes
- PMID: 25789975
- PMCID: PMC4385943
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2015.67
Long noncoding RNA lincRNA-p21 is the major mediator of UVB-induced and p53-dependent apoptosis in keratinocytes
Abstract
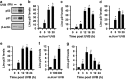
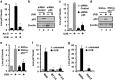
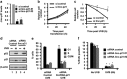
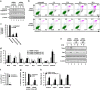
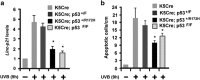
LincRNA-p21 is a long noncoding RNA and a transcriptional target of p53 and HIF-1α. LincRNA-p21 regulates gene expression in cis and trans, mRNA translation, protein stability, the Warburg effect, and p53-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in doxorubicin-treated mouse embryo fibroblasts. p53 plays a key role in the response of skin keratinocytes to UVB-induced DNA damage by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In skin cancer development, UVB-induced mutation of p53 allows keratinocytes upon successive UVB exposures to evade apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. We hypothesized that lincRNA-p21 has a key functional role in UVB-induced apoptosis and/or cell cycle arrest in keratinocytes and loss of lincRNA-p21 function results in the evasion of apoptosis and/or cell cycle arrest. We observed that lincRNA-p21 transcripts are highly inducible by UVB in mouse and human keratinocytes in culture and in mouse skin in vivo. LincRNA-p21 is regulated at the transcriptional level in response to UVB, and the UVB induction of lincRNA-p21 in keratinocytes and in vivo in mouse epidermis is primarily through a p53-dependent pathway. Knockdown of lincRNA-p21 blocked UVB-induced apoptosis in mouse and human keratinocytes, and lincRNA-p21 was responsible for the majority of UVB-induced and p53-mediated apoptosis in keratinocytes. Knockdown of lincRNA-p21 had no effect on cell proliferation in untreated or UVB-treated keratinocytes. An early event in skin cancer is the mutation of a single p53 allele. We observed that a mutant p53(+/R172H) allele expressed in mouse epidermis (K5Cre(+/tg);LSLp53(+/R172H)) showed a significant dominant-negative inhibitory effect on UVB-induced lincRNA-p21 transcription and apoptosis in epidermis. We conclude lincRNA-p21 is highly inducible by UVB and has a key role in triggering UVB-induced apoptotic death. We propose that the mutation of a single p53 allele provides a pro-oncogenic function early in skin cancer development through a dominant inhibitory effect on UVB-induced lincRNA-p21 expression and the subsequent evasion of UVB-induced apoptosis.
Figures
References
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS, Urban AE, Zhu X, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
-
- Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science. 2007;316:1484–1488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

