In vitro γ-ray-induced inflammatory response is dominated by culturing conditions rather than radiation exposures
- PMID: 25791775
- PMCID: PMC4366819
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09343
In vitro γ-ray-induced inflammatory response is dominated by culturing conditions rather than radiation exposures
Abstract
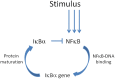
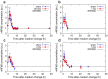
The inflammatory pathway has a pivotal role in regulating the fate and functions of cells after a wide range of stimuli, including ionizing radiation. However, the molecular mechanisms governing such responses have not been completely elucidated yet. In particular, the complex activation dynamics of the Nuclear transcription Factor kB (NF-kB), the key molecule governing the inflammatory pathway, still lacks a complete characterization. In this work we focused on the activation dynamics of the NF-kB (subunit p65) pathway following different stimuli. Quantitative measurements of NF-kB were performed and results interpreted within a systems theory approach, based on the negative feedback loop feature of this pathway. Time-series data of nuclear NF-kB concentration showed no evidence of γ-ray induced activation of the pathway for doses up to 5 Gy but highlighted important transient effects of common environmental stress (e.g. CO2, temperature) and laboratory procedures, e.g. replacing the culture medium, which dominate the in vitro inflammatory response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular delineation of gamma-ray-induced NF-kappaB activation and pro-inflammatory genes in SMP30 knockout mice.Radiat Res. 2010 May;173(5):629-34. doi: 10.1667/RR1629.1. Radiat Res. 2010. PMID: 20426662
-
Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in human lymphoblastoid cells by low-dose ionizing radiation.Radiat Res. 1994 Jun;138(3):367-72. Radiat Res. 1994. PMID: 8184011
-
Dose-dependent biphasic induction and transcriptional activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) in EA.hy.926 endothelial cells after low-dose X-irradiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2004 Feb;80(2):115-23. doi: 10.1080/09553000310001654701. Int J Radiat Biol. 2004. PMID: 15164793
-
Aging-induced up-regulation of nuclear binding activities of oxidative stress responsive NF-kB transcription factor in mouse cardiac muscle.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996 Mar;28(3):487-98. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0045. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 9011632
-
[Nf-kB transcription factor: role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory, autoimmune, and neoplastic diseases and therapy implications].Clin Ter. 2001 Jul-Aug;152(4):249-53. Clin Ter. 2001. PMID: 11725618 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
The Interplay between Radioresistant Caco-2 Cells and the Immune System Increases Epithelial Layer Permeability and Alters Signaling Protein Spectrum.Front Immunol. 2017 Mar 3;8:223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00223. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28316601 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Injected Human Stem Cells Enhance Rehabilitation in TBI Mice Via Modulation of Survival and Inflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;55(6):4870-4884. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0683-3. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28736792 Free PMC article.
-
NCEH-1 modulates cholesterol metabolism and protects against α-synuclein toxicity in a C. elegans model of Parkinson's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Oct 1;26(19):3823-3836. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx269. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28934392 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB oscillations translate into functionally related patterns of gene expression.Elife. 2016 Jan 14;5:e09100. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09100. Elife. 2016. PMID: 26765569 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals Targeting Oxidative Stress, Interconnected Neuroinflammatory, and Neuroapoptotic Pathways Following Radiation.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(5):836-856. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210809103346. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34370636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Courtois G. & Gilmore T. D. Mutations in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway: implications for human disease. Oncogene 25, 6831–43 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Sen R. & Baltimore D. Multiple Nuclear Factors Interact with the Immunoglobulin Enhancer. Cell 46, 705–716 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann A. & Baltimore D. Circuitry of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Immunol. Rev. 210, 171–86 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Oeckinghaus A., Hayden M. S. & Ghosh S. Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 12, 695–708 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Tkach K. E., Oyler J. E. & Altan-Bonnet G. Cracking the NF-κB code. Sci. Signal. 7, pe5 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

