Distinct type I and type II toxin-antitoxin modules control Salmonella lifestyle inside eukaryotic cells
- PMID: 25792384
- PMCID: PMC4366850
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09374
Distinct type I and type II toxin-antitoxin modules control Salmonella lifestyle inside eukaryotic cells
Abstract
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules contribute to the generation of non-growing cells in response to stress. These modules abound in bacterial pathogens although the bases for this profusion remain largely unknown. Using the intracellular bacterial pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium as a model, here we show that a selected group of TA modules impact bacterial fitness inside eukaryotic cells. We characterized in this pathogen twenty-seven TA modules, including type I and type II TA modules encoding antisense RNA and proteinaceous antitoxins, respectively. Proteomic and gene expression analyses revealed that the pathogen produces numerous toxins of TA modules inside eukaryotic cells. Among these, the toxins HokST, LdrAST, and TisBST, encoded by type I TA modules and T4ST and VapC2ST, encoded by type II TA modules, promote bacterial survival inside fibroblasts. In contrast, only VapC2ST shows that positive effect in bacterial fitness when the pathogen infects epithelial cells. These results illustrate how S. Typhimurium uses distinct type I and type II TA modules to regulate its intracellular lifestyle in varied host cell types. This function specialization might explain why the number of TA modules increased in intracellular bacterial pathogens.
Figures

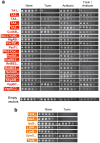
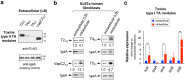
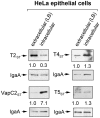
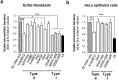
References
-
- Bravo A., de Torrontegui G. & Diaz R. Identification of components of a new stability system of plasmid R1, ParD, that is close to the origin of replication of this plasmid. Mol. Gen. Genet. 210, 101–110 (1987). - PubMed
-
- Gerdes K. in Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxins (Springer, 2013).
-
- Hayes F. & Van Melderen L. Toxins-antitoxins: diversity, evolution and function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 46, 386–408 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

