Extensive microRNA-mediated crosstalk between lncRNAs and mRNAs in mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 25792609
- PMCID: PMC4417114
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.181974.114
Extensive microRNA-mediated crosstalk between lncRNAs and mRNAs in mouse embryonic stem cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Extensive microRNA-mediated crosstalk between lncRNAs and mRNAs in mouse embryonic stem cells.Genome Res. 2015 Sep;25(9):1410.1. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26330573 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
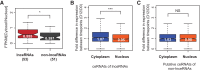
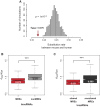
Recently, a handful of intergenic long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to compete with mRNAs for binding to miRNAs and to contribute to development and disease. Beyond these reports, little is yet known of the extent and functional consequences of miRNA-mediated regulation of mRNA levels by lncRNAs. To gain further insight into lncRNA-mRNA miRNA-mediated crosstalk, we reanalyzed transcriptome-wide changes induced by the targeted knockdown of over 100 lncRNA transcripts in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). We predicted that, on average, almost one-fifth of the transcript level changes induced by lncRNAs are dependent on miRNAs that are highly abundant in mESCs. We validated these findings experimentally by temporally profiling transcriptome-wide changes in gene expression following the loss of miRNA biogenesis in mESCs. Following the depletion of miRNAs, we found that >50% of lncRNAs and their miRNA-dependent mRNA targets were up-regulated coordinately, consistent with their interaction being miRNA-mediated. These lncRNAs are preferentially located in the cytoplasm, and the response elements for miRNAs they share with their targets have been preserved in mammals by purifying selection. Lastly, miRNA-dependent mRNA targets of each lncRNA tended to share common biological functions. Post-transcriptional miRNA-mediated crosstalk between lncRNAs and mRNA, in mESCs, is thus surprisingly prevalent, conserved in mammals, and likely to contribute to critical developmental processes.
© 2015 Tan et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Bartel DP. 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
