Crystal structure of barley limit dextrinase-limit dextrinase inhibitor (LD-LDI) complex reveals insights into mechanism and diversity of cereal type inhibitors
- PMID: 25792743
- PMCID: PMC4432282
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.642777
Crystal structure of barley limit dextrinase-limit dextrinase inhibitor (LD-LDI) complex reveals insights into mechanism and diversity of cereal type inhibitors
Abstract
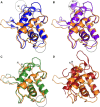
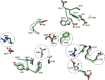
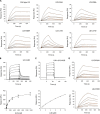
Molecular details underlying regulation of starch mobilization in cereal seed endosperm remain unknown despite the paramount role of this process in plant growth. The structure of the complex between the starch debranching enzyme barley limit dextrinase (LD), hydrolyzing α-1,6-glucosidic linkages, and its endogenous inhibitor (LDI) was solved at 2.7 Å. The structure reveals an entirely new and unexpected binding mode of LDI as compared with previously solved complex structures of related cereal type family inhibitors (CTIs) bound to glycoside hydrolases but is structurally analogous to binding of dual specificity CTIs to proteases. Site-directed mutagenesis establishes that a hydrophobic cluster flanked by ionic interactions in the protein-protein interface is vital for the picomolar affinity of LDI to LD as assessed by analysis of binding by using surface plasmon resonance and also supported by LDI inhibition of the enzyme activity. A phylogenetic analysis identified four LDI-like proteins in cereals among the 45 sequences from monocot databases that could be classified as unique CTI sequences. The unprecedented binding mechanism shown here for LDI has likely evolved in cereals from a need for effective inhibition of debranching enzymes having characteristic open active site architecture. The findings give a mechanistic rationale for the potency of LD activity regulation and provide a molecular understanding of the debranching events associated with optimal starch mobilization and utilization during germination. This study unveils a hitherto not recognized structural basis for the features endowing diversity to CTIs.
Keywords: Barley Limit Dextrinase; Cereal Type Inhibitors; Crystal Structure; Debranching Enzyme; Enzyme Inhibitor; Plant Molecular Biology; Protein Complex; Protein-Protein Interaction; Seed Germination; Starch Metabolism Regulation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Tester R. F., Karkalas J., Qi X. (2004) Starch: composition, fine structure and architecture. J. Cereal Sci. 39, 151–165
-
- Sulpice R., Pyl E. T., Ishihara H., Trenkamp S., Steinfath M., Witucka-Wall H., Gibon Y., Usadel B., Poree F., Piques M. C., Von Korff M., Steinhauser M. C., Keurentjes J. J., Guenther M., Hoehne M., Selbig J., Fernie A. R., Altmann T., Stitt M. (2009) Starch as a major integrator in the regulation of plant growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 10348–10353 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeeman S. C., Kossmann J., Smith A. M. (2010) Starch: Its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 61, 209–234 - PubMed
-
- Kristensen M., Lok F., Planchot V., Svendsen I., Leah R., Svensson B. (1999) Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding the starch debranching enzyme limit dextrinase from germinating barley. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1431, 538–546 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

