Effect of keishibukuryogan on genetic and dietary obesity models
- PMID: 25793003
- PMCID: PMC4352422
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/801291
Effect of keishibukuryogan on genetic and dietary obesity models
Abstract
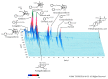
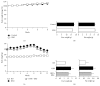
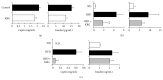
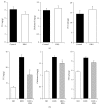
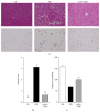
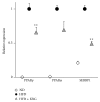
Obesity has been recognized as one of the most important risk factors for a variety of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension/cardiovascular diseases, steatosis/hepatitis, and cancer. Keishibukuryogan (KBG, Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan in Chinese) is a traditional Chinese/Japanese (Kampo) medicine that has been known to improve blood circulation and is also known for its anti-inflammatory or scavenging effect. In this study, we evaluated the effect of KBG in two distinct rodent models of obesity driven by either a genetic (SHR/NDmcr-cp rat model) or dietary (high-fat diet-induced mouse obesity model) mechanism. Although there was no significant effect on the body composition in either the SHR rat or the DIO mouse models, KBG treatment significantly decreased the serum level of leptin and liver TG level in the DIO mouse, but not in the SHR rat model. Furthermore, a lower fat deposition in liver and a smaller size of adipocytes in white adipose tissue were observed in the DIO mice treated with KBG. Importantly, we further found downregulation of genes involved in lipid metabolism in the KBG-treated liver, along with decreased liver TG and cholesterol level. Our present data experimentally support in fact that KBG can be an attractive Kampo medicine to improve obese status through a regulation of systemic leptin level and/or lipid metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review on the Mechanism and Application of Keishibukuryogan.Front Nutr. 2021 Dec 24;8:760918. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.760918. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 35004802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keishibukuryogan (gui-zhi-fu-ling-wan), a Kampo formula, decreases disease activity and soluble vascular adhesion molecule-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006 Sep;3(3):359-64. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nel025. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006. PMID: 16951720 Free PMC article.
-
The traditional Japanese formula keishibukuryogan reduces liver injury and inflammation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Mar;1190:151-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05265.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20388146
-
Identification of a predictive biomarker for the beneficial effect of keishibukuryogan, a kampo (Japanese traditional) medicine, on patients with climacteric syndrome.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:962109. doi: 10.1155/2014/962109. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24639885 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Obesity.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Sep 25;13:3371-3381. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S274534. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33061498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review on the Mechanism and Application of Keishibukuryogan.Front Nutr. 2021 Dec 24;8:760918. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.760918. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 35004802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GZFLW Induces Apoptosis of Ectopic Endometrial Stromal Cells via Promoting VPS53 Protein Stability.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Dec 13;2018:1293630. doi: 10.1155/2018/1293630. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30643524 Free PMC article.
-
The Multiple Pharmacologic Functions and Mechanisms of Action of Guizhi Fuling Formulation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 29;2022:6813421. doi: 10.1155/2022/6813421. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35529925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leung L., Kang J., Rayyan E., et al. Decreased basal chloride secretion and altered cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulatory protein, Villin, GLUT5 protein expression in jejunum from leptin-deficient mice. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity. 2014;7:321–330. doi: 10.2147/dmso.s63714. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

