Periodic Fever: a review on clinical, management and guideline for Iranian patients - part I
- PMID: 25793039
- PMCID: PMC4359590
Periodic Fever: a review on clinical, management and guideline for Iranian patients - part I
Abstract
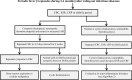
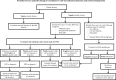
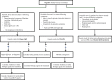
Periodic fever syndromes are a group of diseases characterized by episodes of fever with healthy intervals between febrile episodes. The first manifestation of these disorders are present in childhood and adolescence, but infrequently it may be presented in young and middle ages. Genetic base has been known for all types of periodic fever syndromes except periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and cervical adenitis (PFAPA). Common periodic fever disorders are Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) and PFAPA. In each patient with periodic fever, acquired infection with chronic and periodic nature should be ruled out. It depends on epidemiology of infectious diseases. Some of them such as Familial Mediterranean fever and PFAPA are common in Iran. In Iran and other Middle East countries, brucellosis, malaria and infectious mononucleosis should be considered in differential diagnosis of periodic fever disorders especially with fever and arthritis manifestation. In children, urinary tract infection may be presented as periodic disorder, urine analysis and culture is necessary in each child with periodic symptoms. Some malignancies such as leukemia and tumoral lesions should be excluded in patients with periodic syndrome and weight loss in any age. After excluding infection, malignancy and cyclic neutropenia, FMF and PFAPA are the most common periodic fever disorders. Similar to other countries, Hyper IgD, Chronic Infantile Neurologic Cutaneous and Articular, TRAPS and other auto-inflammatory syndromes are rare causes of periodic fever in Iranian system registry. In part 1 of this paper we reviewed the prevalence of FMF and PFAPA in Iran. In part 2, some uncommon auto-inflammatory disorders such as TRAPS, Hyper IgD sydrome and cryopyrin associated periodic syndromes will be reviewed.
Keywords: Familial Mediterranean Fever; Hyper IgD; PFAPA; Periodic Fever; TRAPS.
Figures
References
-
- Grateau G, Duruoz MT. Autoinflammatory conditions: when to suspect? How to treat? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol . 2010;24(3):40–11. - PubMed
-
- Montealegre Sanchez G, Hashkez PJ. Neurological manifestations of the Mendelian-inherited autoinflammatory syndromes. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009;51(6):420–8. - PubMed
-
- Simon A, van der Meer JW. Pathogenesis of familial periodic fever syndromes or hereditary autoinflammatory syndromes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292(1):R86–98. - PubMed
-
- Long SS. Distinguishing among prolonged, recurrent, and periodic fever syndromes: approach of a pediatric infectious diseases subspecialist. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2005;52(3):811–35. - PubMed
-
- Barron K, Athreya B, Kastner D. Periodic fever syndromes and other inherited autoinflammatory diseases. In: Cassidy JT, Petty RE, Laxer RM, et al., editors. Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Sanders; 2011. pp. 642–60.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources