Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of etanercept in patients with moderately active rheumatoid arthritis despite DMARD therapy
- PMID: 25793152
- PMCID: PMC4359699
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-015-0895-9
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of etanercept in patients with moderately active rheumatoid arthritis despite DMARD therapy
Abstract
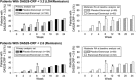
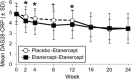
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of adding etanercept to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in patients with moderately active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (ClinicalTrials.gov #NCT01313208) enrolled RA patients with Disease Activity Score using 28 joints with C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) >3.2 and ≤5.1 (moderate disease) despite stable DMARD therapy. Patients were randomized to etanercept 50 mg or placebo weekly for 12 weeks; all patients then received etanercept 50 mg weekly through week 24. Primary endpoint was low disease activity (LDA) at week 12; secondary endpoints included DAS28-CRP remission at week 12; Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) and Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) LDA; American College of Rheumatology (ACR) responses; change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and safety. For 210 patients with moderate disease at screening, (104 placebo; 106 etanercept), only 58% still had moderate disease at baseline. At week 12, 33% on etanercept and 21% on placebo achieved LDA (P = 0.055); remission was achieved in 19% and 12%, respectively (P = 0.14). At week 12, ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses were observed in 29%, 13%, and 1% respectively, in patients on placebo, and 41%, 21%, and 6% of patients on etanercept. Mean (SD) change from baseline in HAQ-DI score was -0.20 (0.43) for placebo patients and -0.39 (0.54) for etanercept patients at week 12. No new safety signals were observed. LDA was achieved by more patients on etanercept than placebo in patients with moderate disease at screening, but the difference was not statistically significant at week 12.
Keywords: Etanercept; Randomized controlled trial; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures

References
-
- Aletaha D, Smolen J. The Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI): a review of their usefulness and validity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23:S100–S108. - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, Medsger TA, Jr, Mitchell DM, Neustadt DH, Pinals RS, Schaller JG, Sharp JT, Wilder RL, Hunder GG. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, Markenson J, Finck BK. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1586–1593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432201. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, Katz LM, Lightfoot R, Jr, Paulus H, Strand V, Tugwell P, Weinblatt M, Williams HJ, Wolfe F, Kieszak S. American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:727–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380602. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fransen J, van Riel PL. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23:S93–S99. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

