Blood-based protein biomarker panel for the detection of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 25793510
- PMCID: PMC4368610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120425
Blood-based protein biomarker panel for the detection of colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: The majority of colorectal cancer (CRC) cases are preventable by early detection and removal of precancerous polyps. Even though CRC is the second most common internal cancer in Australia, only 30 per cent of the population considered to have risk factors participate in stool-based test screening programs. Evidence indicates a robust, blood-based, diagnostic assay would increase screening compliance. A number of potential diagnostic blood-based protein biomarkers for CRC have been reported, but all lack sensitivity or specificity for use as a stand-alone diagnostic. The aim of this study was to identify and validate a panel of protein-based biomarkers in independent cohorts that could be translated to a reliable, non-invasive blood-based screening test.
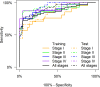
Principal findings: In two independent cohorts (n = 145 and n = 197), we evaluated seven single biomarkers in serum of CRC patients and age/gender matched controls that showed a significant difference between controls and CRC, but individually lack the sensitivity for diagnostic application. Using logistic regression strategies, we identified a panel of three biomarkers that discriminated between controls and CRC with 73% sensitivity at 95% specificity, when applied to either of the two cohorts. This panel comprised of Insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2), Dickkopf-3 (DKK3), and Pyruvate kinase M2(PKM2).
Conclusions: Due to the heterogeneous nature of CRC, a single biomarker is unlikely to have sufficient sensitivity or specificity for use as a stand-alone diagnostic screening test and a panel of markers may be more effective. We have identified a 3 biomarker panel that has higher sensitivity and specificity for early stage (Stage I and -II) disease than the faecal occult blood test, raising the possibility for its use as a non-invasive blood diagnostic or screening test.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research 2007. Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective Washington, DC: American Institute for Cancer Research.
-
- Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990;61: 759–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous