Experimental butchering of a chimpanzee carcass for archaeological purposes
- PMID: 25793521
- PMCID: PMC4368797
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121208
Experimental butchering of a chimpanzee carcass for archaeological purposes
Erratum in
-
Correction: Experimental butchering of a chimpanzee carcass for archaeological purposes.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 17;10(4):e0126785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126785. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25886570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
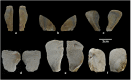
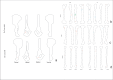
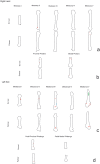
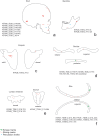
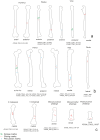
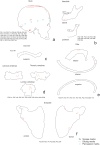
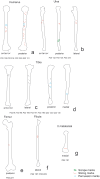
Two archaeological assemblages from the Sierra de Atapuerca sites show evidence of anthropogenic cannibalism. These are the late Early Pleistocene level TD6-2 at Gran Dolina, and the Bronze Age level MIR4 in the Mirador Cave. Despite the chronological distance between these two assemblages, they share the common feature that the human remains exhibit a high frequency of anthropogenic modifications (cut marks, percussion pits and notches and peeling). This frequency could denote special treatment of bodies, or else be the normal result of the butchering process. In order to test these possibilities, we subjected a chimpanzee carcass to a butchering process. The processing was intensive and intended to simulate preparation for consumption. In doing this, we used several simple flakes made from quartzite and chert from quarries in the Sierra de Atapuerca. The skull, long bones, metapodials and phalanges were also fractured in order to remove the brain and bone marrow. As a result, about 40% of the remains showed some kind of human modification. The frequency, distribution and characteristics of these modifications are very similar to those documented on the remains of Homo antecessor from TD6-2. In case of the MIR4 assemblage, the results are similar except in the treatment of skulls. Our results indicate that high frequencies of anthropogenic modifications are common after an intensive butchering process intended to prepare a hominin body for consumption in different contexts (both where there was possible ritual behavior and where this was not the case and the modifications are not the result of special treatment).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


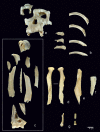

Similar articles
-
Intergroup cannibalism in the European Early Pleistocene: the range expansion and imbalance of power hypotheses.J Hum Evol. 2012 Nov;63(5):682-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Sep 1. J Hum Evol. 2012. PMID: 22944348
-
Carcass transport decisions in Homo antecessor subsistence strategies.J Hum Evol. 2011 Oct;61(4):425-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 Jul 28. J Hum Evol. 2011. PMID: 21802117
-
Human cannibalism in the Early Pleistocene of Europe (Gran Dolina, Sierra de Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain).J Hum Evol. 1999 Sep-Oct;37(3-4):591-622. doi: 10.1006/jhev.1999.0324. J Hum Evol. 1999. PMID: 10497001
-
Evidence for bronze age cannibalism in El Mirador Cave (Sierra de Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain).Am J Phys Anthropol. 2007 Jul;133(3):899-917. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.20610. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2007. PMID: 17492670
-
Zooarchaeology and taphonomy of Aurora Stratum (Gran Dolina, Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain).J Hum Evol. 1999 Sep-Oct;37(3-4):623-52. doi: 10.1006/jhev.1999.0346. J Hum Evol. 1999. PMID: 10497002
Cited by
-
New insights of cultural cannibalism amongst Magdalenian groups at Maszycka Cave, Poland.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 6;15(1):2351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86093-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39915582 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of neolithic cannibalism among farming communities at El Mirador cave, Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 7;15(1):26648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10266-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40774979 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Experimental butchering of a chimpanzee carcass for archaeological purposes.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 17;10(4):e0126785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126785. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25886570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Shedding light on the Early Pleistocene of TD6 (Gran Dolina, Atapuerca, Spain): The technological sequence and occupational inferences.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 25;13(1):e0190889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190889. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29370188 Free PMC article.
-
Early Pleistocene cut marked hominin fossil from Koobi Fora, Kenya.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 26;13(1):9896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35702-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37365179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cáceres I, Lozano M, Saladié P. Evidence for Bronze Age cannibalism in El Mirador cave (Sierra de Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain). Am J Phys Anthropol. 2007; 133: 899–917. - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Jalvo Y, Díez JC, Cáceres I, Rosell J. Human cannibalism in the Early Pleistocene of Europe (Gran Dolina, Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain). J Hum Evol. 1999; 37: 591–622. - PubMed
-
- Saladié P. Mossegades d'omnívors Aproximació experimental i aplicació zooarqueològica als jaciments de la Sierra de Atapuerca. 2009; Tarragona: Universitat Rovira i Virgili; Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Palmira_Saladie/publications?pubTyp... 10.7399/FH.2013.37.6.1077.[Hypolipidemic - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

