Tenascin-X: beyond the architectural function
- PMID: 25793578
- PMCID: PMC4422802
- DOI: 10.4161/19336918.2014.994893
Tenascin-X: beyond the architectural function
Abstract
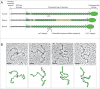
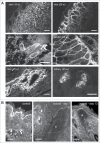
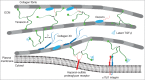
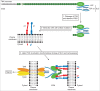
Tenascin-X is the largest member of the tenascin (TN) family of evolutionary conserved extracellular matrix glycoproteins, which also comprises TN-C, TN-R and TN-W. Among this family, TN-X is the only member described so far to exert a crucial architectural function as evidenced by a connective tissue disorder (a recessive form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) resulting from a loss-of-function of this glycoprotein in humans and mice. However, TN-X is more than an architectural protein, as it displays features of a matricellular protein by modulating cell adhesion. However, the cellular functions associated with the anti-adhesive properties of TN-X have not yet been revealed. Recent findings indicate that TN-X is also an extracellular regulator of signaling pathways. Indeed, TN-X has been shown to regulate the bioavailability of the Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-β and to modulate epithelial cell plasticity. The next challenges will be to unravel whether the signaling functions of TN-X are functionally linked to its matricellular properties.
Keywords: ECM, extracellular matrix; EDS, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS); FAK, focal adhesion kinase; FBG, fibrinogen-like domain; FNIII, fibronectin type III module; LAP, latency associated peptide; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; SLC, small latent complex; TGF-β; TGF-β activation; TN, tenascin; TSP-1, thrombospondin-1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; cell signaling; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT); integrin α11β1; matricellular protein; tenascin-X; transforming growth factor-β.
Figures
References
-
- Morel Y, Bristow J, Gitelman SE, Miller WL. Transcript encoded on the opposite strand of the human steroid 21-hydroxylase/complement component C4 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1989; 86:6582-6; PMID:2475872; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.17.6582 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto K, Arai M, Ishihara N, Ando A, Inoko H, Ikemura T. Cluster of fibronectin type III repeats found in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region shows the highest homology with the repeats in an extracellular matrix protein, tenascin. Genomics 1992; 12:485-91; PMID:1373119; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0888-7543(92)90438-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto K, Ishihara N, Ando A, Inoko H, Ikemura T. Extracellular matrix protein tenascin-like gene found in human MHC class III region. Immunogenetics 1992; 36:400-3; PMID:1382042; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00218048 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bristow J, Tee MK, Gitelman SE, Mellon SH, Miller WL. Tenascin-X: a novel extracellular matrix protein encoded by the human XB gene overlapping P450c21B. J Cell Biol 1993; 122:265-78; PMID:7686164; http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.122.1.265 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Mackie EJ, Pearson CA, Sakakura T. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein involved in tissue interactions during fetal development and oncogenesis. Cell 1986; 47:131-9; PMID:2428505; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(86)90374-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
