Effect of the interplay between trauma severity and trait neuroticism on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms among adolescents exposed to a pipeline explosion
- PMID: 25793606
- PMCID: PMC4368575
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120493
Effect of the interplay between trauma severity and trait neuroticism on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms among adolescents exposed to a pipeline explosion
Abstract
Background: While numerous studies have explored relevant factors of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms, there have been few joint investigations of trauma severity and trait neuroticism on the development of PTSD symptoms. This study aims to assess the involvement and interrelationship of trauma severity and neuroticism in the expression of PTSD symptoms among adolescents exposed to an accidental explosion.
Methods: Six hundred and sixty-two adolescents were recruited from a junior middle school closest to the 2013 pipeline explosion site in China and were assessed using the Explosion Exposure Questionnaire, the NEO Five Factor Inventory-Neuroticism Subscale (FFI-N), and the PTSD Checklist-Civilian (PCL-C). A battery of hierarchical multiple regression analyses and two-way ANOVAs were performed to examine the effect of trauma severity and trait neuroticism on adolescent PTSD symptoms.
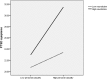
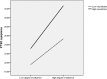
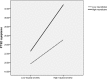
Results: Eighty-seven adolescents (13.1%) showed PTSD symptoms after the pipeline explosion. Correlation analysis showed that all the factors of explosion exposure and trait neuroticism were positively associated with adolescent PTSD symptoms. Being male and younger was linked to lower risk for PTSD symptoms. The regression models identified explosion exposure and neuroticism as independent risk factors for PTSD symptoms, and the interactions between trait neuroticism and trauma exposure (personal casualty, degree of influence, total traumatic severity) were related to PTSD symptoms.
Conclusions: The results highlight the role of trauma exposure and trait neuroticism as risk factors for PTSD symptoms. Therefore, the combination of these two factors should be investigated in clinical settings due to an augmented risk for more severe PTSD symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chou FH, Wu HC, Chou P, Su CY, Tsai KY, Chao SS, et al. (2007) Epidemiologic psychiatric studies on post-disaster impact among Chi-Chi earthquake survivors in Yu-Chi, Taiwan. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 61(4): 370–8. - PubMed
-
- Sun YP, Dong ZJ, Yi MJ, Sun DF (2006) Childhood sexual abuse among 1307 adult students and analysis on results of the Symptom Checklist-90. Chin J Pediatr 44(1): 21–5. - PubMed
-
- Sar V, Akyuz G, Kugu N, Ozturk E, Ertem-Vehid H (2006) Axis I dissociative disorder comorbidity in borderline personality disorder and reports of childhood trauma. J Clin Psychiatry 67(10): 1583–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

