Determining microvascular obstruction and infarct size with steady-state free precession imaging cardiac MRI
- PMID: 25793609
- PMCID: PMC4368429
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119788
Determining microvascular obstruction and infarct size with steady-state free precession imaging cardiac MRI
Abstract
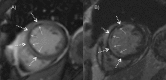
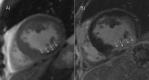
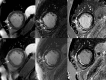
Purpose: In cardiac MRI (cMRI) injection of contrast medium may be performed prior to the acquisition of cine steady-state free precession (SSFP) imaging to speed up the protocol and avoid delay before late Gadolinium enhancement (LGE) imaging. Aim of this study was to evaluate whether a condensed clinical protocol with contrast cine SSFP imaging is able to detect early microvascular obstruction (MO) and determine the infarct size compared to the findings of LGE inversion recovery sequences.
Materials and methods: The study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki and was performed following approval by the ethic committee of the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg. Written informed consent was obtained from every patient. 68 consecutive patients (14 females/54 males) with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) treated by percutaneous coronary revascularization were included in this study. CMRI was performed 6.6±2 days after symptom onset and MO and infarct size in early contrast SSFP cine imaging were compared to LGE imaging.
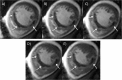
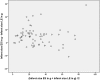
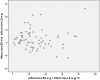
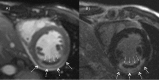
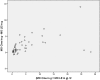
Results: MO was detected in 47/68 (69%) patients on cine SSFP and in 41/68 (60%) patients on LGE imaging. In 6 patients MO was found on cine SSFP imaging but was not detectable on LGE imaging. Infarct size on cine SSFP showed a strong agreement to LGE imaging (intraclass correlation coefficient [ICC] of 0.96 for enddiastolic, p<0.001 and 0.96 for endsystolic, p<0.001 respectively). Significant interobserver agreement was found measuring enddiastolic and endsystolic infarct size on cine SSFP imaging (p<0.01).
Conclusions: In patients after STEMI infarct size and presence of MO can be detected with contrast cine SSFP imaging. This could be an option in patients who are limited in their ability to comply with the demands of a cMRI protocol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sheehan FH, Doerr R, Schmidt WG, Bolson EL, Uebis R, von Essen R, et al. Early recovery of left ventricular function after thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: an important determinant of survival. J Am Coll Cardiol 1988;12: 289–300. - PubMed
-
- Grines CL, Cox DA, Stone GW, Garcia E, Mattos LA, Giambartolomei A, et al. Coronary angioplasty with or without stent implantation for acute myocardial infarction. Stent Primary Angioplasty in Myocardial Infarction Study Group. N Engl J Med 1999; 341 1949–56. - PubMed
-
- Ito H, Tomooka T, Sakai N, Yu H, Higashino Y, Fujii K, et al. Lack of myocardial perfusion immediately after successful thrombolysis. A predictor of poor recovery of left ventricular function in anterior myocardial infarction. Circulation 1992;85: 1699–1705. - PubMed
-
- Ito H, Maruyama A, Iwakura K, Takiuchi S, Masuyama T, Hori M, et al. Clinical implications of the "no-reflow" phenomenon. A predictor of complications and left ventricular remodeling in reperfused anterior wall myocardial infarction. Circulation 1996;93: 223–228. - PubMed
-
- Wu KC, Zerhouni EA, Judd RM, Lugo-Olivieri CH, Barouch LA, Schulman SP, et al. Prognostic significance of microvascular obstruction by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 1998;97: 765–772. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

