RMND5 from Xenopus laevis is an E3 ubiquitin-ligase and functions in early embryonic forebrain development
- PMID: 25793641
- PMCID: PMC4368662
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120342
RMND5 from Xenopus laevis is an E3 ubiquitin-ligase and functions in early embryonic forebrain development
Abstract
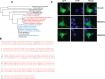
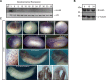
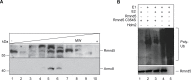
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae the Gid-complex functions as an ubiquitin-ligase complex that regulates the metabolic switch between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In higher organisms six conserved Gid proteins form the CTLH protein-complex with unknown function. Here we show that Rmnd5, the Gid2 orthologue from Xenopus laevis, is an ubiquitin-ligase embedded in a high molecular weight complex. Expression of rmnd5 is strongest in neuronal ectoderm, prospective brain, eyes and ciliated cells of the skin and its suppression results in malformations of the fore- and midbrain. We therefore suggest that Xenopus laevis Rmnd5, as a subunit of the CTLH complex, is a ubiquitin-ligase targeting an unknown factor for polyubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation for proper fore- and midbrain development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Regelmann J, Schule T, Josupeit FS, Horak J, Rose M, Entian KD, et al. Catabolite degradation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a genome-wide screen identifies eight novel GID genes and indicates the existence of two degradation pathways. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14(4):1652–63. Epub 2003/04/11. 10.1091/mbc.E02-08-0456 PubMed PMID: . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Menssen R, Schweiggert J, Schreiner J, Kusevic D, Reuther J, Braun B, et al. Exploring the Topology of the Gid Complex, the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Involved in Catabolite-induced Degradation of Gluconeogenic Enzymes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(30):25602–14. Epub 2012/05/31. 10.1074/jbc.M112.363762 PubMed PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braun B, Pfirrmann T, Menssen R, Hofmann K, Scheel H, Wolf DH. Gid9, a second RING finger protein contributes to the ubiquitin ligase activity of the Gid complex required for catabolite degradation. FEBS Lett. 2011. Epub 2011/11/03. S0014-5793(11)00789-7 [pii]10.1016/j.febslet.2011.10.038 PubMed PMID: . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santt O, Pfirrmann T, Braun B, Juretschke J, Kimmig P, Scheel H, et al. The yeast GID complex, a novel ubiquitin ligase (E3) involved in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(8):3323–33. Epub 2008/05/30. E08-03-0328 [pii]10.1091/mbc.E08-03-0328 PubMed PMID: . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

