Effect of intravenous sodium valproate vs dexamethasone on acute migraine headache: a double blind randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 25793707
- PMCID: PMC4368536
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120229
Effect of intravenous sodium valproate vs dexamethasone on acute migraine headache: a double blind randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Despite the impact of sodium valproate and dexamethasone on migraine headache, the efficacy of the two drugs has not been properly investigated and compared. This trial compared the effect of the two drugs on acute migraine headache.
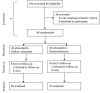
Methods: This double blind randomized clinical trial was conducted on patients aged 18 to 65 years with acute migraine headache who referred to the emergency departments of Beasat and Farshchian Hospitals in Hamadan, Iran, from April 2012 to June 2014. Patients were randomly assigned to receive a single-dose of either 400 mg sodium valproate or 16 mg dexamethasone plus 50 ml saline normal solution within 15 min intravenously. The severity of headache in the two groups was evaluated at baseline, 0.5 and 2 hours later using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) on a scale of 0 to 10.
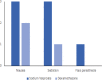
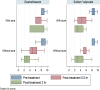
Results: Of 104 patients enrolled, 72 patients remained for analysis. The effect of both sodium valproate and dexamethasone on acute migraine headache was statistically significant at 0.5 and 2 hours post-treatment compared to pre-treatment (P=0.001). The severity of headache based on VAS reduced form 8.20 (7.72, 8.68) before treatment to 5.31 (4.74, 5.89) and 3.66 (2.99, 4.33) at 0.5 and 2 hours after treatment, respectively, in patients receiving sodium valproate and from 8.46 (8.05, 8.86) before treatment to 5.46 (4.81, 6.11) and 3.59 (2.84, 4.35) at 0.5 and 2 hours after treatment, respectively, in patients receiving dexamethasone. Both drugs were highly effective in improvement of acute headache in patients without aura. However, sodium valproate significantly improved the acute headache in patients with aura but dexamethasone did not. The severity of headache based on VAS reduced form 8.50 (7.40, 9.60) before treatment to 4.67 (2.40, 6.93) and 3.50 (1.78, 5.22) at 0.5 and 2 hours after treatment, respectively, in patients with aura receiving sodium valproate and from 8.80 (7.76, 9.84) before treatment to 7.20 (4.98, 9.42) and 6.20 (2.43, 9.97) at 0.5 and 2 hours after treatment, respectively, in patients with aura receiving dexamethasone.
Conclusions: This trial indicated that, in overall, intravenous sodium valproate is not superior to intravenous dexamethasone in treatment of acute migraine attacks. However, in patients with aura, only sodium valproate but not dexamethasone is effective in headache relief. This issue needs further investigations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov IRCT201202199014N1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Friedman BW, Hochberg ML, Esses D, Grosberg B, Corbo J, Toosi B, et al. Applying the International Classification of Headache Disorders to the emergency department: an assessment of reproducibility and the frequency with which a unique diagnosis can be assigned to every acute headache presentation. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49(4): 409–419. - PubMed
-
- Vinson DR. Treatment patterns of isolated benign headache in US emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2002;39(3): 215–222. - PubMed
-
- Friedman BW. IV Valproate for Acute Migraine. A Randomized Comparison Versus IV Metoclopramide and IV Ketorolac New York: ClinicalTrials.gov; 2014 [updated 9 August 2014; cited 10 August 2014]. Available from: http://www.clinicalconnection.com/exp/EPVS.aspx?studyID=300719&slID=7480210.
-
- Kozubski W, Prusinski A. The comparison of sodium valproate and ergotamine titrate plus caffeine in the abortive treatment of migraine attacks. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 1995;29(6): 929–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

