Phosphorylation of lamins determine their structural properties and signaling functions
- PMID: 25793944
- PMCID: PMC4615644
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2015.1017167
Phosphorylation of lamins determine their structural properties and signaling functions
Abstract
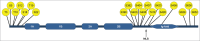
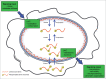
Lamin A/C is part of the nuclear lamina, a meshwork of intermediate filaments underlying the inner nuclear membrane. The lamin network is anchoring a complex set of structural and linker proteins and is either directly or through partner proteins also associated or interacting with a number of signaling protein and transcription factors. During mitosis the nuclear lamina is dissociated by well established phosphorylation- dependent mechanisms. A-type lamins are, however, also phosphorylated during interphase. A recent study identified 20 interphase phosphorylation sites on lamin A/C and explored their functions related to lamin dynamics; movements, localization and solubility. Here we discuss these findings in the light of lamin functions in health and disease.
Keywords: EDMD, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IFs, intermediate filaments; LAP2α, Lamina-associated polypeptide 2 isoform α; intermediate filaments; lamin A/C; laminopathy; lamins; phosphorylation; signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Hyder CL, Isoniemi KO, Torvaldson ES, Eriksson JE. Insights into intermediate filament regulation from development to ageing. J Cell Sci 2011; 124:1363-72; PMID:21502133; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1242/jcs.041244 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eriksson JE, Dechat T, Grin B, Helfand B, Mendez M, Pallari H-M, Goldman RD. Introducing intermediate filaments: from discovery to disease. J Clin Invest 2009; 119:1763-71; PMID:19587451; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1172/JCI38339 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dechat T, Pfleghaar K, Sengupta K, Shimi T, Shumaker DK, Solimando L, Goldman RD. Nuclear lamins: major factors in the structural organization and function of the nucleus and chromatin. Genes Dev 2008; 22:832-53; PMID:18381888; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/gad.1652708 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gesson K, Vidak S, Foisner R. Lamina-associated polypeptide (LAP)2? and nucleoplasmic lamins in adult stem cell regulation and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; 29:116-24; PMID:24374133; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.12.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
