Improvement in renal function and its impact on survival in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- PMID: 25794132
- PMCID: PMC4382661
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2015.20
Improvement in renal function and its impact on survival in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
Abstract
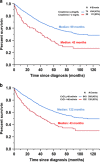
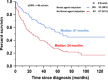
Renal impairment (RI) is seen in over a quarter of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). It is not clear if reversal of RI improves the outcome to that expected for NDMM patients without RI. We evaluated 1135 consecutive patients with NDMM seen at the Mayo Clinic between January 2003 and December 2012. RI was defined as having a creatinine clearance (CrCl) <40ml/min. The median overall survival (OS) for patients with RI at diagnosis receiving and not receiving novel agent induction therapy was not reached vs 46 months (P<0.001). The median OS for patients with CrCl ⩾40 ml/min at diagnosis, CrCl <40 ml/min at diagnosis but improved to ⩾40 ml/min and CrCl <40 ml/min at diagnosis and remained <40 ml/min, were 112, 56 and 33 months, respectively (P<0.001). The complete renal response rate for patients with RI at diagnosis receiving novel agent induction therapy compared to the rest was 40 vs 16% (P<0.001). In conclusion, patients with reversal of RI have improved outcomes, but it remains inferior to patients with normal renal function at diagnosis. These results have implications for identifying early treatment strategies for patients at risk of developing renal insufficiency.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, et al. Review of 1027 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78:21–33. - PubMed
-
- Knudsen LM, Hippe E, Hjorth M, Holmberg E, Westin J. Renal function in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma—a demographic study of 1353 patients. The Nordic Myeloma Study Group. Eur J Haematol. 1994;53:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1860–1873. - PubMed
-
- Alexanian R, Barlogie B, Dixon D. Renal failure in multiple myeloma. Pathogenesis and prognostic implications. Arch Intern Med. 1990;150:1693–1695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

