NEDDylation is essential for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency and lytic reactivation and represents a novel anti-KSHV target
- PMID: 25794275
- PMCID: PMC4368050
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004771
NEDDylation is essential for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency and lytic reactivation and represents a novel anti-KSHV target
Abstract
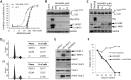
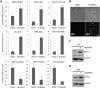
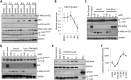
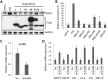
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the causative agent of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), which are aggressive malignancies associated with immunocompromised patients. For many non-viral malignancies, therapeutically targeting the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) has been successful. Likewise, laboratory studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the UPS might provide a promising avenue for the treatment of KSHV-associated diseases. The largest class of E3 ubiquitin ligases are the cullin-RING ligases (CRLs) that are activated by an additional ubiquitin-like protein, NEDD8. We show that pharmacological inhibition of NEDDylation (using the small molecule inhibitor MLN4924) is cytotoxic to PEL cells by inhibiting NF-κB. We also show that CRL4B is a novel regulator of latency as its inhibition reactivated lytic gene expression. Furthermore, we uncovered a requirement for NEDDylation during the reactivation of the KSHV lytic cycle. Intriguingly, inhibition prevented viral DNA replication but not lytic cycle-associated gene expression, highlighting a novel mechanism that uncouples these two features of KSHV biology. Mechanistically, we show that MLN4924 treatment precluded the recruitment of the viral pre-replication complex to the origin of lytic DNA replication (OriLyt). These new findings have revealed novel mechanisms that regulate KSHV latency and reactivation. Moreover, they demonstrate that inhibition of NEDDylation represents a novel approach for the treatment of KSHV-associated malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of the NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor MLN4924 on Lytic Reactivation of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus.J Virol. 2017 Sep 12;91(19):e00505-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00505-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28701396 Free PMC article.
-
ARID3B: a Novel Regulator of the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Cycle.J Virol. 2016 Sep 29;90(20):9543-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03262-15. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27512077 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Vpr Inhibits Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication by Inducing MicroRNA miR-942-5p and Activating NF-κB Signaling.J Virol. 2016 Sep 12;90(19):8739-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00797-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27440900 Free PMC article.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
-
Regulation of KSHV Latency and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):1034. doi: 10.3390/v12091034. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32957532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The cellular chloride channels CLIC1 and CLIC4 contribute to virus-mediated cell motility.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 23;293(12):4582-4590. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001343. Epub 2018 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29462791 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of specific inhibitors of SUMO-1- and SUMO-2/3-mediated protein-protein interactions using Affimer (Adhiron) technology.Sci Signal. 2017 Nov 14;10(505):eaaj2005. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaj2005. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 29138295 Free PMC article.
-
Host Cell Neddylation Facilitates Alphaherpesvirus Entry in a Virus-Specific and Cell-Dependent Manner.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0311422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03114-22. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36173301 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Post-translational Modifications in Influenza A Virus Life Cycle and Host Innate Immune Response.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 4;11:517461. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.517461. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33013775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A Regulates the Stability of Cellular Transcripts Required for Efficient KSHV Lytic Replication.Viruses. 2023 Jun 16;15(6):1381. doi: 10.3390/v15061381. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37376680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown HJ, McBride WH, Zack JA, Sun R. Prostratin and bortezomib are novel inducers of latent Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Antivir Ther. 2005;10: 745–751. - PubMed
-
- Matta H, Chaudhary PM. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in primary effusion lymphoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005;4: 77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

