In Vitro, Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic, and Safety Comparisons of Single and Combined Administration of Tiotropium and Salmeterol in COPD Patients Using Different Dry Powder Inhalers
- PMID: 25794622
- PMCID: PMC4476986
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-015-9751-7
In Vitro, Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic, and Safety Comparisons of Single and Combined Administration of Tiotropium and Salmeterol in COPD Patients Using Different Dry Powder Inhalers
Abstract
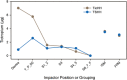
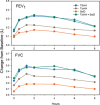
In vitro Andersen cascade impactor-sized mass (ISM) and aerodynamic fine particle mass (FPM) <5 μm for tiotropium and salmeterol combined in a novel inhalation powder formulation containing 7.5 μg tiotropium/25 μg salmeterol (TSHH) were similar (within ±15%) to reference products containing 18 μg of tiotropium (Spiriva® HandiHaler®) (TioHH) and 50 μg of salmeterol (Serevent® Diskus®) (SalD). The pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability of the novel fixed-dose TSHH formulation administered once daily was compared with the single-agent therapies TioHH (once daily [qd]) and SalD (twice daily [bid]) and with the jointly administered combination of TioHH (qd) plus SalD (bid) in a randomized, 22-week, open-label, four-way crossover study in 50 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For tiotropium, TSHH and TioHH were bioequivalent based on mean steady-state plasma area under the plasma concentration-time curves (AUC), while the urinary excretion amount was higher for TSHH and not bioequivalent to TioHH. Tiotropium peak plasma concentrations at steady state (C max,ss) were 40% higher with TSHH. For salmeterol, substantial differences were observed in plasma AUCs and Cmax,ss. No significant differences in 8-h forced expiratory volume in 1 s or forced vital capacity were detected for the TSHH (qd) against the combination of TioHH (qd) with SalD (bid). Maintenance therapy with tiotropium plus salmeterol as TSHH or as the jointly administered reference products is superior to either agent alone, safe, and well tolerated in COPD patients. In vitro results were not predictive of clinical PK findings for both tiotropium and salmeterol for the TSHH dry powder inhaler product.
Figures





References
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(5):1256–76. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.5.2101039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vincken W. Bronchodilator treatment of stable COPD: long-acting anticholinergics. Eur Respir Rev. 2005;14:23–32. doi: 10.1183/09058180.05.00009403. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

