Fibroblast growth factor 21 prevents atherosclerosis by suppression of hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 and induction of adiponectin in mice
- PMID: 25794851
- PMCID: PMC4444420
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015308
Fibroblast growth factor 21 prevents atherosclerosis by suppression of hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 and induction of adiponectin in mice
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a metabolic hormone with pleiotropic effects on glucose and lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. It acts as a key downstream target of both peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and γ, the agonists of which have been used for lipid lowering and insulin sensitization, respectively. However, the role of FGF21 in the cardiovascular system remains elusive.
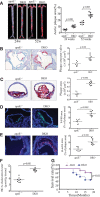
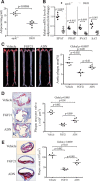
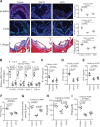
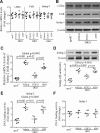
Methods and results: The roles of FGF21 in atherosclerosis were investigated by evaluating the impact of FGF21 deficiency and replenishment with recombinant FGF21 in apolipoprotein E(-/-) mice. FGF21 deficiency causes a marked exacerbation of atherosclerotic plaque formation and premature death in apolipoprotein E(-/-) mice, which is accompanied by hypoadiponectinemia and severe hypercholesterolemia. Replenishment of FGF21 protects against atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E(-/-)mice via 2 independent mechanisms, inducing the adipocyte production of adiponectin, which in turn acts on the blood vessels to inhibit neointima formation and macrophage inflammation, and suppressing the hepatic expression of the transcription factor sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2, thereby leading to reduced cholesterol synthesis and attenuation of hypercholesterolemia. Chronic treatment with adiponectin partially reverses atherosclerosis without obvious effects on hypercholesterolemia in FGF21-deficient apolipoprotein E(-/-) mice. By contrast, the cholesterol-lowering effects of FGF21 are abrogated by hepatic expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2.
Conclusions: FGF21 protects against atherosclerosis via fine tuning the multiorgan crosstalk among liver, adipose tissue, and blood vessels.
Keywords: adipokines; atherosclerosis; fibroblast growth factor 21; hormones.
© 2015 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A, Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers JS, Owens RA, Gromada J, Brozinick JT, Hawkins ED, Wroblewski VJ, Li DS, Mehrbod F, Jaskunas SR, Shanafelt AB. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1627–1635. doi: 10.1172/JCI23606. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARα and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5:426–437. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.05.002. - PubMed
-
- Potthoff MJ, Inagaki T, Satapati S, Ding X, He T, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Finck BN, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Burgess SC. FGF21 induces PGC-1α and regulates carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism during the adaptive starvation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:10853–10858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904187106. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coskun T, Bina HA, Schneider MA, Dunbar JD, Hu CC, Chen Y, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A. Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology. 2008;149:6018–6027. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0816. - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Wroblewski VJ, Koester A, Chen YF, Clutinger CK, Tigno XT, Hansen BC, Shanafelt AB, Etgen GJ. The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology. 2007;148:774–781. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

