Emerging therapeutic targets of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- PMID: 25795498
- PMCID: PMC4369320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2015.01.005
Emerging therapeutic targets of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
Abstract
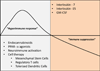
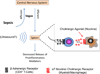
Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SA-AKI) is linked to high morbidity and mortality. To date, singular approaches to target specific pathways known to contribute to the pathogenesis of SA-AKI have failed. Because of the complexity of the pathogenesis of SA-AKI, a reassessment necessitates integrative approaches to therapeutics of SA-AKI that include general supportive therapies such as the use of vasopressors, fluids, antimicrobials, and target-specific and time-dependent therapeutics. There has been recent progress in our understanding of the pathogenesis and treatment of SA-AKI including the temporal nature of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes. In this review, we discuss the clinical and experimental basis of emerging therapeutic approaches that focus on targeting early proinflammatory and late anti-inflammatory processes, as well as therapeutics that may enhance cellular survival and recovery. Finally, we include ongoing clinical trials in sepsis.
Keywords: Inflammation; cytokines; septic shock; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Renal Medullary Hypoxia: A New Therapeutic Target for Septic Acute Kidney Injury?Semin Nephrol. 2019 Nov;39(6):543-553. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2019.10.004. Semin Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31836037 Review.
-
Clinical approach to the patient with AKI and sepsis.Semin Nephrol. 2015 Jan;35(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2015.01.003. Semin Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25795496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: A disease of the microcirculation.Microcirculation. 2019 Feb;26(2):e12483. doi: 10.1111/micc.12483. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Microcirculation. 2019. PMID: 29908046 Review.
-
Sepsis: update in the management.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013 Jan;20(1):6-13. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2012.10.013. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013. PMID: 23265591 Review.
-
Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.Crit Care Clin. 2015 Oct;31(4):649-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Crit Care Clin. 2015. PMID: 26410135 Review.
Cited by
-
Monophosphoryl lipid A prevents impairment of medullary thick ascending limb [Formula: see text] absorption and improves plasma [Formula: see text] concentration in septic mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):F711-F725. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00033.2018. Epub 2018 May 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741098 Free PMC article.
-
The renal level of a novel cytokine IL-35 is related to sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in mice.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Nov 1;10(11):10998-11005. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966444 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Relationship of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Acute Kidney Injury: Causation or Association?Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1094296. doi: 10.1155/2016/1094296. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27006941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Key Genes and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Using Transformer and Machine Learning Approaches.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 May 16;12(5):536. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12050536. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428155 Free PMC article.
-
Update on sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: emerging targeted therapies.Biologics. 2016 Nov 7;10:149-156. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S87385. eCollection 2016. Biologics. 2016. PMID: 27853353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:840–851. - PubMed
-
- Zarjou A, Agarwal A. Sepsis and acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:999–1006. - PubMed
-
- Matejovic M, Chvojka J, Radej J, Ledvinova L, Karvunidis T, Krouzecky A, et al. Sepsis and acute kidney injury are bidirectional. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;174:78–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

