Oscillating Square Wave Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Delivered During Slow Wave Sleep Does Not Improve Declarative Memory More Than Sham: A Randomized Sham Controlled Crossover Study
- PMID: 25795621
- PMCID: PMC4598642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2015.01.414
Oscillating Square Wave Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Delivered During Slow Wave Sleep Does Not Improve Declarative Memory More Than Sham: A Randomized Sham Controlled Crossover Study
Abstract
Background: A 2006 trial in healthy medical students found that anodal slow oscillating tDCS delivered bi-frontally during slow wave sleep had an enhancing effect in declarative, but not procedural memory. Although there have been supporting animal studies, and similar findings in pathological groups, this study has not been replicated, or refuted, in the intervening years. We therefore tested these earlier results for replication using similar methods with the exception of current waveform (square in our study, nearly sinusoidal in the original).
Objective/hypothesis: Our objective was to test the findings of a 2006 trial suggesting bi-frontal anodal tDCS during slow wave sleep enhances declarative memory.
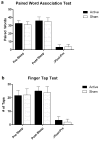
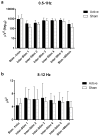
Methods: Twelve students (mean age 25, 9 women) free of medical problems underwent two testing conditions (active, sham) in a randomized counterbalanced fashion. Active stimulation consisted of oscillating square wave tDCS delivered during early Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep. The sham condition consisted of setting-up the tDCS device and electrodes, but not turning it on during sleep. tDCS was delivered bi-frontally with anodes placed at F3/F4, and cathodes placed at mastoids. Current density was 0.517 mA/cm(2), and oscillated between zero and maximal current at a frequency of 0.75 Hz. Stimulation occurred during five-five minute blocks with 1-min inter-block intervals (25 min total stimulation). The primary outcomes were both declarative memory consolidation measured by a paired word association test (PWA), and non-declarative memory, measured by a non-dominant finger-tapping test (FTT). We also recorded and analyzed sleep EEG.
Results: There was no difference in the number of paired word associations remembered before compared to after sleep [(active = 3.1 ± 3.0 SD more associations) (sham = 3.8 ± 3.1 SD more associations)]. Finger tapping improved, (non-significantly) following active stimulation [(3.6 ± 2.7 SD correctly typed sequences) compared to sham stimulation (2.3 ± 2.2 SD correctly typed sequences)].
Conclusion: In this study, we failed to find improvements in declarative or performance memory and could not replicate an earlier study using nearly identical settings. Specifically we failed to find a beneficial effect on either overnight declarative or non-declarative memory consolidation via square-wave oscillating tDCS intervention applied bi-frontally during early NREM sleep. It is unclear if the morphology of the tDCS pulse is critical in any memory related improvements.
Keywords: Cognitive enhancement; Memory consolidation; Sleep; Slow wave sleep; Transcranial direct current stimulation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Slow oscillatory transcranial direct current stimulation (so-tDCS) during slow wave sleep has no effects on declarative memory in healthy young subjects.Brain Stimul. 2019 Jul-Aug;12(4):948-958. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2019.02.012. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Brain Stimul. 2019. PMID: 30842037
-
Boosting Slow Oscillatory Activity Using tDCS during Early Nocturnal Slow Wave Sleep Does Not Improve Memory Consolidation in Healthy Older Adults.Brain Stimul. 2016 Sep-Oct;9(5):730-739. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Brain Stimul. 2016. PMID: 27247261 Clinical Trial.
-
No effects of slow oscillatory transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on sleep-dependent memory consolidation in healthy elderly subjects.Brain Stimul. 2013 Nov;6(6):938-45. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Brain Stimul. 2013. PMID: 23810208 Clinical Trial.
-
Can Slow-Wave Sleep Enhancement Improve Memory? A Review of Current Approaches and Cognitive Outcomes.Yale J Biol Med. 2019 Mar 25;92(1):63-80. eCollection 2019 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30923474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcranial electrical stimulation during sleep enhances declarative (but not procedural) memory consolidation: Evidence from a meta-analysis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Apr;63:65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.01.009. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 26828569 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting sleep oscillations to improve memory in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2020 Jul;221:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.01.010. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 32014359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive brain stimulation and neuroenhancement.Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2022 May 25;7:146-165. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2022.05.002. eCollection 2022. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35734582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving working memory by electrical stimulation and cross-frequency coupling.Mol Brain. 2024 Oct 1;17(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01142-1. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 39354549 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Sleep Oscillations and Their Functional Coupling by Transcranial Stimulation Enhances Memory Consolidation in Mild Cognitive Impairment.J Neurosci. 2017 Jul 26;37(30):7111-7124. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0260-17.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28637840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuromodulation of sleep rhythms in schizophrenia: Towards the rational design of non-invasive brain stimulation.Schizophr Res. 2020 Jul;221:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 32354662 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marshall L, Helgadottir H, Molle M, Born J. Boosting slow oscillations during sleep potentiates memory. Nature. 2006;444:610–613. - PubMed
-
- Antonenko D, Diekelmann S, Olsen C, Born J, Molle M. Napping to renew learning capacity: enhanced encoding after stimulation of sleep slow oscillations. Eur J Neurosci. 2013;37:1142–1151. - PubMed
-
- Goder R, Baier PC, Beith B, Baecker C, Seeck-Hirschner M, et al. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation during sleep on memory performance in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2013;144:153–154. - PubMed
-
- Prehn-Kristensen A, Munz M, Goder R, Wilhelm I, Korr K, et al. Transcranial Oscillatory Direct Current Stimulation During Sleep Improves Declarative Memory Consolidation in Children With Attention-deficit/hyperactivity Disorder to a Level Comparable to Healthy Controls. Brain Stimul 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

