A rare case of bilateral nasolabial cysts
- PMID: 25795742
- PMCID: PMC4368954
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203543
A rare case of bilateral nasolabial cysts
Abstract
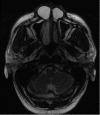
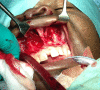
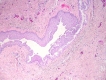
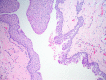
Nasolabial cysts are rare non-odontogenic cystic lesions representing around 0.7% of all maxillofacial cysts. They usually present as unilateral painless swellings, sometimes with epiphora and dacryocystitis as well as pain in cases of rapid growth or infection. We have reviewed the literature and present an extremely rare case of bilateral nasolabial cysts in a young Afro-Caribbean man presenting with chronic nasal blockage, epiphora and rhinorrhoea. We describe our successful surgical management using a sublabial approach for complete excision, leading to a disease-free outcome at 6 months follow-up. Other modalities have been described, from endoscopic marsupialisation to simple aspiration. However, with the exception of complete surgical excision, all other surgical techniques are associated with a high recurrence rate. We therefore advocate complete surgical excision as described below for optimal results.
2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical