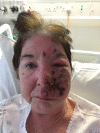
Trigeminal herpes zoster: early recognition and treatment are crucial
- PMID: 25795749
- PMCID: PMC4369019
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-208673
Trigeminal herpes zoster: early recognition and treatment are crucial
Abstract
Reactivation of varicella zoster virus (VZV) is not uncommon in older patients, particularly in cases of chronic autoimmune disorders and in patients taking immunosuppressant drugs. We present a case of a 57-year-old woman presenting with severe herpes zoster infection, involving the maxillary and ophthalmic branches of the trigeminal nerve. Despite an initial delay in instigating crucial antiviral treatment, the patient achieved an excellent recovery, with only some mild scarring at 2 months postinfection. Trigeminal herpes zoster is a potentially devastating clinical occurrence, and is associated with severe long-term neurological sequelae, including encephalitis, vision loss and postherpetic neuralgia. Physicians must be aware of risk factors and treatment modalities.
2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Souto A, Maneiro JR, Salgado E et al. . Risk of tuberculosis in patients with chronic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases treated with biologics and tofacitinib: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and longterm extension studies. Rheumatology 2014;53:1872–85. 10.1093/rheumatology/keu172 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical