BRCA1 regulates PIG3-mediated apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner
- PMID: 25797244
- PMCID: PMC4480703
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3263
BRCA1 regulates PIG3-mediated apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner
Abstract
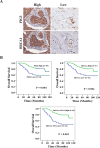
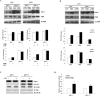
BRCA1 plays a key role in the regulation of p53-dependent target gene transcription activation. Meanwhile, the p53 inducible gene 3 (PIG3) is a downstream target of p53 and is involved in p53-initiated apoptosis. However, little is known about whether BRCA1 can regulate PIG3-mediated apoptosis. Using a tissue microarray containing 149 breast cancer patient samples, we found that BRCA1 and PIG3 expression status were significantly positively correlated (r = 0.678, P < 0.001) and identified a significant positive correlation between high expression of BRCA1 and/or PIG3 and overall survival (OS). Moreover, we reveal that overexpression of BRCA1 significantly increased expression of PIG3 in cells with intact p53, whereas no increase in PIG3 was observed in p53-null MDA-MB-157 cells and p53-depleted HCT116p53-/- cells. Meanwhile, ectopic expression of BRCA1 could not lead to an increase expression level of prohibitin (PHB), which we have previously identified to induce PIG3-mediated apoptosis. Finally, ChIP analysis revealed that PHB can bind to the PIG3 promoter and activate PIG3 transcription independent of p53, although p53 presence did enhance this process. Taken together, our findings suggest that BRCA1 regulates PIG3-mediated apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner, and that PIG3 expression is associated with a better OS in breast cancer patients.
Keywords: BRCA1; PIG3; breast cancer; p53; prohibitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

