Overcoming T cell exhaustion in infection and cancer
- PMID: 25797516
- PMCID: PMC4393798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2015.02.008
Overcoming T cell exhaustion in infection and cancer
Abstract
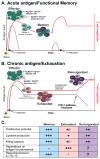
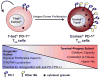
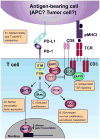
Inhibitors of the Programmed Cell Death 1: Programmed Cell Death 1 ligand 1 (PD-1:PD-L1) pathway, a central regulator of T cell exhaustion, have been recently shown to be effective for treatment of different cancers. However, clinical responses are mixed, highlighting the need to better understand the mechanisms of action of PD-1:PD-L1, the role of this pathway in immunity to different tumors, and the molecular and cellular effects of PD-1 blockade. Here, we review the molecular regulation of T cell exhaustion, placing recent findings on PD-1 blockade therapies in cancer in the context of the broader understanding of the roles of the PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in T cell exhaustion during chronic infection. We discuss the current understanding of the mechanisms involved in reversing T cell exhaustion, and outline critical areas of focus for future research, both basic and clinical.
Keywords: PD-1; PD-L1; T cell exhaustion; cancer; chronic infection; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

