Modulation of expression of genes involved in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and lysosome biogenesis by flavonoids
- PMID: 25797591
- PMCID: PMC4369724
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09378
Modulation of expression of genes involved in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and lysosome biogenesis by flavonoids
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Modulation of expression of genes involved in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and lysosome biogenesis by flavonoids.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 31;6:22809. doi: 10.1038/srep22809. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27029434 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Corrigendum: Modulation of expression of genes involved in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and lysosome biogenesis by flavonoids.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 9;6:38118. doi: 10.1038/srep38118. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27934862 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
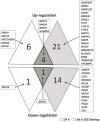
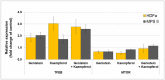
Flavonoids were found previously to modulate efficiency of synthesis of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), compounds which are accumulated in cells of patients suffering from mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs). The aim of this work was to determine effects of different flavonoids (genistein, kaempferol, daidzein) used alone or in combinations, on expression of genes coding for proteins involved in GAG metabolism. Analyses with DNA microarray, followed by real-time qRT-PCR revealed that genistein, kaempferol and combination of these two compounds induced dose- and time-dependent remarkable alterations in transcript profiles of GAG metabolism genes in cultures of wild-type human dermal fibroblasts (HDFa). Interestingly, effects of the mixture of genistein and kaempferol were stronger than those revealed by any of these compounds used alone. Similarly, the most effective reduction in levels of GAG production, in both HDFa and MPS II cells, was observed in the presence of genistein, keampferol and combination of these compounds. Forty five genes were chosen for further verification not only in HDFa, but also in MPS II fibroblasts by using real-time qRT-PCR. Despite effects on GAG metabolism-related genes, we found that genistein, kaempferol and mixture of these compounds significantly stimulated expression of TFEB. Additionally, a decrease in MTOR transcript level was observed at these conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures






References
-
- Neufeld E. & Muenzer J. The mucopolysaccharidoses. Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease III, 3421–3452 (2001).
-
- Kloska A., Jakobkiewicz-Banecka J., Narajczyk M., Banecka-Majkutewicz Z. & Wegrzyn G. Effects of flavonoids on glycosaminoglycan synthesis: implications for substrate reduction therapy in Sanfilippo disease and other mucopolysaccharidoses. Metab Brain Dis 26, 1–8, 10.1007/s11011-011-9233-2 (2011). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

