Value of renal cortical thickness as a predictor of renal function impairment in chronic renal disease patients
- PMID: 25798002
- PMCID: PMC4366023
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2014.0008
Value of renal cortical thickness as a predictor of renal function impairment in chronic renal disease patients
Abstract
Objective: To determine the presence of linear relationship between renal cortical thickness, bipolar length, and parenchymal thickness in chronic kidney disease patients presenting with different estimated glomerular filtration rates (GFRs) and to assess the reproducibility of these measurements using ultrasonography.
Materials and methods: Ultrasonography was performed in 54 chronic renal failure patients. The scans were performed by two independent and blinded radiologists. The estimated GFR was calculated using the Cockcroft-Gault equation. Interobserver agreement was calculated and a linear correlation coefficient (r) was determined in order to establish the relationship between the different renal measurements and estimated GFR.
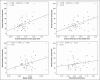
Results: The correlation between GFR and measurements of renal cortical thickness, bipolar length, and parenchymal thickness was, respectively, moderate (r = 0.478; p < 0.001), poor (r = 0.380; p = 0.004), and poor (r = 0.277; p = 0.116). The interobserver agreement was considered excellent (0.754) for measurements of cortical thickness and bipolar length (0.833), and satisfactory for parenchymal thickness (0.523).
Conclusion: The interobserver reproducibility for renal measurements obtained was good. A moderate correlation was observed between estimated GFR and cortical thickness, but bipolar length and parenchymal thickness were poorly correlated.
Objetivo: Determinar se existe relação linear entre a espessura do córtex renal, comprimento bipolar e a espessura do parênquima renal em pacientes com insuficiência renal crônica que apresentam diferentes taxas de filtração glomerular (TFGs) e avaliar a reprodutibilidade dessas medidas.
Materiais e métodos: Exames ultrassonográficos foram realizados em 54 pacientes com insuficiência renal crônica, por dois radiologistas, de modo independente e duplo-cego. A estimativa da TFG foi calculada pela equação de Cockcroft-Gault. A concordância interobservador e o coeficiente de correlação linear (r) foram calculados para estabelecer se existe relação entre medidas renais e a TFG.
Resultados: A espessura do córtex renal apresentou moderada correlação com a TFG (r = 0,478; p < 0,001). O comprimento bipolar e a espessura do parênquima apresentaram fraca correlação, com valores de r = 0,380 (p = 0,004) e r = 0,277 (p = 0,116), respectivamente. A concordância interobservador foi excelente para a espessura cortical (0,754) e comprimento bipolar (0,833) e satisfatória para a espessura do parênquima (0,523).
Conclusão: A reprodutibilidade das medidas obtidas entre os radiologistas foi boa. A relação entre a TFG estimada com a espessura do córtex renal apresentou moderada correlação e o comprimento bipolar e a espessura do parênquima renal apresentaram fraca correlação.
Keywords: Chronic renal disease; Chronic renal failure; Glomerular filtration rate; Renal cortex; Ultrasonography.
Figures
References
-
- Lederer E, Ouseph R. Chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:162–171. - PubMed
-
- Kariyanna SS, Light RP, Agarwal R. A longitudinal study of kidney structure and function in adults. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:1120–1126. - PubMed
-
- Beland MD, Walle NL, Machan JT, et al. Renal cortical thickness measured at ultrasound: is it better than renal length as an indicator of renal function in chronic kidney disease? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195:W146–W149. - PubMed
-
- Emamian SA, Nielsen MB, Pedersen JF, et al. Kidney dimensions at sonography: correlation with age, sex, and habitus in 665 adult volunteers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993;160:83–86. - PubMed
-
- Raj DS, Hoisala R, Somiah S, et al. Quantitation of change in the medullary compartment in renal allograft by ultrasound. J Clin Ultrasound. 1997;25:265–269. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources