Comparison of standardized uptake values measured on F-NaF PET/CT scans using three different tube current intensities
- PMID: 25798003
- PMCID: PMC4366024
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2014.0034
Comparison of standardized uptake values measured on F-NaF PET/CT scans using three different tube current intensities
Abstract
Objective: To analyze standardized uptake values (SUVs) using three different tube current intensities for attenuation correction on (18)FNaF PET/CT scans.
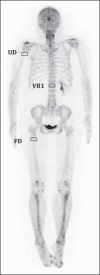
Materials and methods: A total of 254 (18)F-NaF PET/CT studies were analyzed using 10, 20 and 30 mAs. The SUVs were calculated in volumes of interest (VOIs) drawn on three skeletal regions, namely, right proximal humeral diaphysis (RH), right proximal femoral diaphysis (RF), and first lumbar vertebra (LV1) in a total of 712 VOIs. The analyses covered 675 regions classified as normal (236 RH, 232 RF, and 207 LV1).
Results: Mean SUV for each skeletal region was 3.8, 5.4 and 14.4 for RH, RF, and LV1, respectively. As the studies were grouped according to mAs value, the mean SUV values were 3.8, 3.9 and 3.7 for 10, 20 and 30 mAs, respectively, in the RH region; 5.4, 5.5 and 5.4 for 10, 20 and 30 mAs, respectively, in the RF region; 13.8, 14.9 and 14.5 for 10, 20 and 30 mAs, respectively, in the LV1 region.
Conclusion: The three tube current values yielded similar results for SUV calculation.
Objetivo: Analisar os valores de captação (SUVs) utilizando três diferentes intensidades de mAs para realização de correção de atenuação na 18F-NaF PET/CT.
Materiais e métodos: Um total de 254 exames de 18F-NaF PET/CT foi estudado utilizando 10, 20 e 30 mAs. Os SUVs foram calculados utilizando volumes de interesse (VOIs) desenhados em três regiões do esqueleto: diáfise proximal do úmero direito (UD), diáfise proximal do fêmur direito (FD) e primeira vértebra lombar (VB1), totalizando 712 VOIs. Desse total, 675 regiões classificadas como normal foram analisadas (236, 232 e 207 na UD, FD e VB1, respectivamente).
Resultados: A média dos SUVs para cada região óssea foi 3,8, 5,4 e 14,4 para UD, FD e VB1, respectivamente. Quando os exames foram agrupados pelo valor da corrente mAs, a média de valores de captação foi 3,8, 3,9 e 3,7 para 10, 20 e 30 mAs, respectivamente, na UD; 5,4, 5,5 e 5,4 para 10, 20 e 30 mAs, respectivamente, na FD; e 13,8, 14,9 e 14,5 para 10, 20 e 30 mAs, respectivamente, na VB1.
Conclusão: As três correntes analizadas apresentaram resultados similares para o cálculo de SUV.
Keywords: 18F-NaF PET/CT; Corrente de tubo; SUV; Tube current; mAs.
Figures
References
-
- Segall G, Delbeke D, Stabin MG, et al. SNM practice guideline for sodium 18F-fluoride PET/CT bone scans 1.0. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1813–1820. - PubMed
-
- Grant FD, Fahey FH, Packard AB, et al. Skeletal PET with 18Ffluoride: applying new technology to an old tracer. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:68–78. - PubMed
-
- Perkins A, Hilson A, Hall J. Global shortage of medical isotopes threatens nuclear medicine services. BMJ. 2008;337: - PubMed
-
- Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Flusser G, et al. Assessment of malignant skeletal disease: initial experience with 18F-fluoride PET/CT and comparison between 18F-fluoride PET and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:272–278. - PubMed
-
- Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Mishani E, et al. The detection of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer: 99mTc-MDP Planar bone scintigraphy, single- and multi-field-of-view SPECT, 18F-fluoride PET, and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:287–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials