Protective effect of butylated hydroxylanisole against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes
- PMID: 25798044
- PMCID: PMC4367145
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.1.17
Protective effect of butylated hydroxylanisole against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes
Abstract
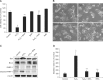
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) is a synthetic phenolic compound consisting of a mixture of two isomeric organic compounds: 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole. We examined the effect of BHA against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced apoptosis in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes. Cell viability was significantly decreased by H2O2 in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, H2O2 treatment increased Bax, decreased Bcl-2, and promoted PARP-1 cleavage in a dose-dependent manner. Pretreatment with BHA before exposure to H2O2 significantly attenuated the H2O2-induced decrease of cell viability. H2O2 exposure resulted in an increase of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation that was significantly inhibited by pretreatment with BHA or N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC, an ROS scavenger). H2O2-induced decrease of cell viability was also attenuated by pretreatment with BHA and NAC. Furthermore, H2O2-induced increase of Bax, decrease of Bcl-2, and PARP-1 cleavage was also inhibited by BHA. Taken together, results of this investigation demonstrated that BHA protects primary cultured mouse hepatocytes against H2O2-induced apoptosis by inhibiting ROS generation.
Keywords: apoptosis; butylated hydroxyanisole; primary mouse hepatocytes; reactive oxygen species.
Figures



References
-
- Aviram M. Review of human studies on oxidative damage and antioxidant protection related to cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic Res. 2000;33(Suppl):S85–S97. - PubMed
-
- Cole KK, Perez-Polo JR. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition prevents both apoptotic-like delayed neuronal death and necrosis after H2O2 injury. J Neurochem. 2002;82:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Conde de la Rosa L, Schoemaker MH, Vrenken TE, Buist-Homan M, Havinga R, Jansen PLM, Moshage H. Superoxide anions and hydrogen peroxide induce hepatocyte death by different mechanisms: involvement of JNK and ERK MAP kinases. J Hepatol. 2006;44:918–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

