Bart syndrome
- PMID: 25798401
- PMCID: PMC4366711
- DOI: 10.5999/aps.2015.42.2.243
Bart syndrome
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
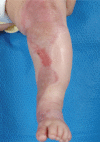
Figures


References
-
- Bart BJ, Gorlin RJ, Anderson VE, et al. Congenital localized absence of skin and associated abnormalities resembling epidermolysis bullosa. A new syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1966;93:296–304. - PubMed
-
- Browning JC. Aplasia cutis congenita: approach to evaluation and management. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:439–444. - PubMed
-
- Elluru RG, Contreras JM, Albert DM. Management of manifestations of epidermolysis bullosa. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;21:588–593. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

