Identification of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR experiments in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha
- PMID: 25798897
- PMCID: PMC4370483
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118678
Identification of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR experiments in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha
Abstract
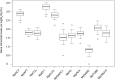
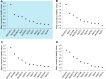
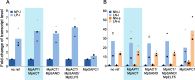
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) has become widely used as a method to compare gene transcript levels across different conditions. However, selection of suitable reference genes to normalize qPCR data is required for accurate transcript level analysis. Recently, Marchantia polymorpha has been adopted as a model for the study of liverwort development and land plant evolution. Identification of appropriate reference genes has therefore become a necessity for gene expression studies. In this study, transcript levels of eleven candidate reference genes have been analyzed across a range of biological contexts that encompass abiotic stress, hormone treatment and different developmental stages. The consistency of transcript levels was assessed using both geNorm and NormFinder algorithms, and a consensus ranking of the different candidate genes was then obtained. MpAPT and MpACT showed relatively constant transcript levels across all conditions tested whereas the transcript levels of other candidate genes were clearly influenced by experimental conditions. By analyzing transcript levels of phosphate and nitrate starvation reporter genes, we confirmed that MpAPT and MpACT are suitable reference genes in M. polymorpha and also demonstrated that normalization with an inappropriate gene can lead to erroneous analysis of qPCR data.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
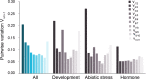
Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha reveals that R2R3MYB activation of flavonoid production in response to abiotic stress is an ancient character in land plants.New Phytol. 2018 Apr;218(2):554-566. doi: 10.1111/nph.15002. Epub 2018 Jan 24. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 29363139
-
Transcriptional Framework of Male Gametogenesis in the Liverwort Marchantia polymorpha L.Plant Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb;57(2):325-38. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw005. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26858289
-
Characterization of four nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase sigma factor genes in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha: blue-light- and multiple stress-responsive SIG5 was acquired early in the emergence of terrestrial plants.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Oct;54(10):1736-48. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct119. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23975891
-
The Naming of Names: Guidelines for Gene Nomenclature in Marchantia.Plant Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb;57(2):257-61. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv193. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26644462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation in Marchantia polymorpha.New Phytol. 2019 Jul;223(2):575-581. doi: 10.1111/nph.15818. Epub 2019 Apr 30. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 30920664 Review.
Cited by
-
Origin and evolution of the nuclear auxin response system.Elife. 2018 Mar 27;7:e33399. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33399. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29580381 Free PMC article.
-
MpWIP regulates air pore complex development in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha.Development. 2017 Apr 15;144(8):1472-1476. doi: 10.1242/dev.144287. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Development. 2017. PMID: 28174248 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochrome Signaling Is Mediated by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR in the Liverwort Marchantia polymorpha.Plant Cell. 2016 Jun;28(6):1406-21. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.01063. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27252292 Free PMC article.
-
Plant lineage-specific PIKMIN1 drives APC/CCCS52A2 E3-ligase activity-dependent cell division.Plant Physiol. 2023 Mar 17;191(3):1574-1595. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac528. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36423220 Free PMC article.
-
The Orthology Clause in the Next Generation Sequencing Era: Novel Reference Genes Identified by RNA-seq in Humans Improve Normalization of Neonatal Equine Ovary RT-qPCR Data.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 4;10(11):e0142122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142122. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26536597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Guenin S, Pelloux J, Lefebvre JF, Louvet R, et al. The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol J. 2008;6: 609–618. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00346.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

