Genome-wide transcript profiling reveals novel breast cancer-associated intronic sense RNAs
- PMID: 25798919
- PMCID: PMC4370647
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120296
Genome-wide transcript profiling reveals novel breast cancer-associated intronic sense RNAs
Abstract
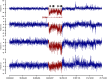
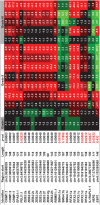
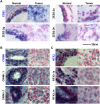
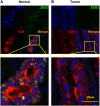
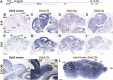
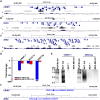
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play major roles in development and cancer progression. To identify novel ncRNAs that may identify key pathways in breast cancer development, we performed high-throughput transcript profiling of tumor and normal matched-pair tissue samples. Initial transcriptome profiling using high-density genome-wide tiling arrays revealed changes in over 200 novel candidate genomic regions that map to intronic regions. Sixteen genomic loci were identified that map to the long introns of five key protein-coding genes, CRIM1, EPAS1, ZEB2, RBMS1, and RFX2. Consistent with the known role of the tumor suppressor ZEB2 in the cancer-associated epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), in situ hybridization reveals that the intronic regions deriving from ZEB2 as well as those from RFX2 and EPAS1 are down-regulated in cells of epithelial morphology, suggesting that these regions may be important for maintaining normal epithelial cell morphology. Paired-end deep sequencing analysis reveals a large number of distinct genomic clusters with no coding potential within the introns of these genes. These novel transcripts are only transcribed from the coding strand. A comprehensive search for breast cancer associated genes reveals enrichment for transcribed intronic regions from these loci, pointing to an underappreciated role of introns or mechanisms relating to their biology in EMT and breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cawley S, Bekiranov S, Ng HH, Kapranov P, Sekinger EA, Kampa D, et al. Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2004;116(4):499–509. - PubMed
-
- Sleutels F, Zwart R, Barlow DP. The non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes. Nature. 2002;415(6873):810–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

