TBI server: a web server for predicting ion effects in RNA folding
- PMID: 25798933
- PMCID: PMC4370743
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119705
TBI server: a web server for predicting ion effects in RNA folding
Abstract
Background: Metal ions play a critical role in the stabilization of RNA structures. Therefore, accurate prediction of the ion effects in RNA folding can have a far-reaching impact on our understanding of RNA structure and function. Multivalent ions, especially Mg²⁺, are essential for RNA tertiary structure formation. These ions can possibly become strongly correlated in the close vicinity of RNA surface. Most of the currently available software packages, which have widespread success in predicting ion effects in biomolecular systems, however, do not explicitly account for the ion correlation effect. Therefore, it is important to develop a software package/web server for the prediction of ion electrostatics in RNA folding by including ion correlation effects.
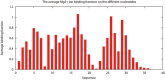
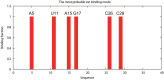
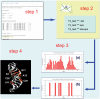
Results: The TBI web server http://rna.physics.missouri.edu/tbi_index.html provides predictions for the total electrostatic free energy, the different free energy components, and the mean number and the most probable distributions of the bound ions. A novel feature of the TBI server is its ability to account for ion correlation and ion distribution fluctuation effects.
Conclusions: By accounting for the ion correlation and fluctuation effects, the TBI server is a unique online tool for computing ion-mediated electrostatic properties for given RNA structures. The results can provide important data for in-depth analysis for ion effects in RNA folding including the ion-dependence of folding stability, ion uptake in the folding process, and the interplay between the different energetic components.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

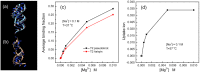
References
-
- Bowman JC, Lenz TK, Hud NV, Williams LD. Cations in charge: magnesium ions in RNA folding and catalysis. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2012;22: 262–272. - PubMed
-
- Ha BY, Thirumalai D. Bending rigidity of stiff polyelectrolyte chains: A single chain and a bundle of multichains. Macromolecules. 2003;36: 9658–9666. 10.1021/ma021226k - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

