Clearance of persistent hepatitis C virus infection in humanized mice using a claudin-1-targeting monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 25798937
- PMCID: PMC4430301
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3179
Clearance of persistent hepatitis C virus infection in humanized mice using a claudin-1-targeting monoclonal antibody
Abstract
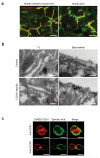
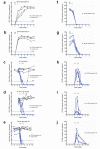
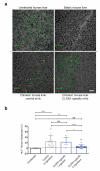
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis and cancer. Cell entry of HCV and other pathogens is mediated by tight junction (TJ) proteins, but successful therapeutic targeting of TJ proteins has not been reported yet. Using a human liver-chimeric mouse model, we show that a monoclonal antibody specific for the TJ protein claudin-1 (ref. 7) eliminates chronic HCV infection without detectable toxicity. This antibody inhibits HCV entry, cell-cell transmission and virus-induced signaling events. Antibody treatment reduces the number of HCV-infected hepatocytes in vivo, highlighting the need for de novo infection by means of host entry factors to maintain chronic infection. In summary, we demonstrate that an antibody targeting a virus receptor can cure chronic viral infection and uncover TJ proteins as targets for antiviral therapy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Hepatitis: Tightening the grip on clearing HCV infection.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 May;12(5):249. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.55. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25850009 No abstract available.
References
-
- Evans MJ, et al. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature. 2007;446:801–805. - PubMed
-
- Fukumatsu M, et al. Shigella targets epithelial tricellular junctions and uses a noncanonical clathrin-dependent endocytic pathway to spread between cells. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;11:325–336. - PubMed
-
- Che P, Tang H, Li Q. The interaction between claudin-1 and dengue viral prM/M protein for its entry. Virology. 2013;446:303–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

