Model-based choices involve prospective neural activity
- PMID: 25799041
- PMCID: PMC4414826
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3981
Model-based choices involve prospective neural activity
Abstract
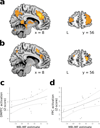
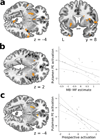
Decisions may arise via 'model-free' repetition of previously reinforced actions or by 'model-based' evaluation, which is widely thought to follow from prospective anticipation of action consequences using a learned map or model. While choices and neural correlates of decision variables sometimes reflect knowledge of their consequences, it remains unclear whether this actually arises from prospective evaluation. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging and a sequential reward-learning task in which paths contained decodable object categories, we found that humans' model-based choices were associated with neural signatures of future paths observed at decision time, suggesting a prospective mechanism for choice. Prospection also covaried with the degree of model-based influences on neural correlates of decision variables and was inversely related to prediction error signals thought to underlie model-free learning. These results dissociate separate mechanisms underlying model-based and model-free evaluation and support the hypothesis that model-based influences on choices and neural decision variables result from prospection.
Figures


References
-
- Thorndike EL. Animal intelligence: an experimental study of the associative processes in animals. Psychol. Rev. Monogr. Suppl. 1898;2:1–8.
-
- Sutton RS, Barto AG. Introduction to Reinforcement Learning. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 1998. at < http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=551283>.
-
- Tolman EC. Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychol. Rev. 1948;55:189–208. - PubMed
-
- Wimmer GE, Shohamy D. Preference by association: how memory mechanisms in the hippocampus bias decisions. Science. 2012;338:270–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

