Role of the sympathetic nervous system in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity and systemic inflammation
- PMID: 25799095
- PMCID: PMC4370606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121365
Role of the sympathetic nervous system in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity and systemic inflammation
Abstract
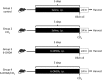
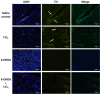
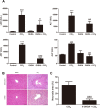
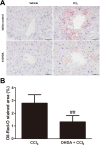
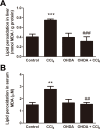
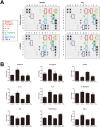
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is widely used as an animal model of hepatotoxicity and the mechanisms have been arduously studied, however, the contribution of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) in CCl4-induced acute hepatotoxicity remains controversial. It is also known that either CCl4 or SNS can affect systemic inflammatory responses. The aim of this study was to establish the effect of chemical sympathectomy with 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in a mouse model of CCl4-induced acute hepatotoxicity and systemic inflammatory response. Mice exposed to CCl4 or vehicle were pretreated with 6-OHDA or saline. The serum levels of aminotransferases and alkaline phosphatase in the CCl4-poisoning mice with sympathetic denervation were significantly lower than those without sympathetic denervation. With sympathetic denervation, hepatocellular necrosis and fat infiltration induced by CCl4 were greatly decreased. Sympathetic denervation significantly attenuated CCl4-induced lipid peroxidation in liver and serum. Acute CCl4 intoxication showed increased expression of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines [eotaxin-2/CCL24, Fas ligand, interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-6, IL-12p40p70, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)], as well as decreased expression of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and keratinocyte-derived chemokine. The overexpressed levels of IL-1α, IL-6, IL-12p40p70, MCP-1/CCL2, and TNF-α were attenuated by sympathetic denervation. Pretreatment with dexamethasone significantly reduced CCl4-induced hepatic injury. Collectively, this study demonstrates that the SNS plays an important role in CCl4-induced acute hepatotoxicity and systemic inflammation and the effect may be connected with chemical- or drug-induced hepatotoxicity and circulating immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
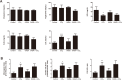

Similar articles
-
Sympathetic Nervous System Control of Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Oxidative Stress in Liver through α-Adrenergic Signaling.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3190617. doi: 10.1155/2016/3190617. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26798417 Free PMC article.
-
Obeticholic acid protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury and inflammation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 1;314:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27865854
-
Preventive effects of the polysaccharide of Larimichthys crocea swim bladder on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic damage.Chin J Nat Med. 2015 Jul;13(7):521-8. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(15)30046-7. Chin J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26233842
-
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for carbon tetrachloride poisoning.Drug Saf. 1991 Sep-Oct;6(5):332-8. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199106050-00003. Drug Saf. 1991. PMID: 1930739 Review.
-
A new direction in the study of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity.Life Sci. 1983 Aug 1;33(5):401-8. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90787-7. Life Sci. 1983. PMID: 6348456 Review.
Cited by
-
SGLT2 Inhibitor-Induced Sympathoexcitation in White Adipose Tissue: A Novel Mechanism for Beiging.Biomedicines. 2020 Nov 18;8(11):514. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8110514. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33218034 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of licochalcone B on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver toxicity in mice.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Aug;19(8):910-915. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27746874 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids Have Opposing Effects on Liver Fibrosis in Hepatic Stellate and Immune Cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Aug;30(8):905-16. doi: 10.1210/me.2016-1029. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27355192 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Liver Sympathetic Nervous System on Liver Fibrosis and Regeneration After Bile Duct Ligation in Rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jan 6;74(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s12031-023-02176-1. J Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38183518
-
Impaired Fas-Fas Ligand Interactions Result in Greater Recurrent Herpetic Stromal Keratitis in Mice.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:435140. doi: 10.1155/2015/435140. Epub 2015 Oct 4. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26504854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2003;33: 105–136. - PubMed
-
- Judah JD, Rees KR. Mechanism of action of carbon tetrachloride. Fed Proc. 1959;18: 1013–1020. - PubMed
-
- Manibusan MK, Odin M, Eastmond DA. Postulated carbon tetrachloride mode of action: a review. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2007;25: 185–209. - PubMed
-
- Smialowicz RJ, Simmons JE, Luebke RW, Allis JW. Immunotoxicologic assessment of subacute exposure of rats to carbon tetrachloride with comparison to hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1991;17: 186–196. - PubMed
-
- Letteron P, Fromenty B, Terris B, Degott C, Pessayre D. Acute and chronic hepatic steatosis lead to in vivo lipid peroxidation in mice. J Hepatol. 1996;24: 200–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

