Isorhamnetin attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage apoptosis via PI3K/AKT activation and HO-1 induction
- PMID: 25799286
- PMCID: PMC4370599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120259
Isorhamnetin attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage apoptosis via PI3K/AKT activation and HO-1 induction
Abstract
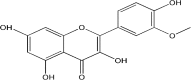
Background and purpose: Isorhamnetin (Iso) is a flavonoid compound extracted from the Chinese herb Hippophae rhamnoides L. Previous studies have revealed its anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant activities. This study investigated the ability of Iso to inhibit oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced cell apoptosis in THP-1-derived macrophages. The effects of Iso on atherosclerosis in vivo were also evaluated in apolipoprotein E knockout (ApoE-/-) mice fed a high fat diet.
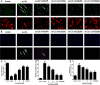
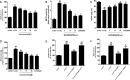
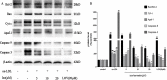
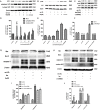
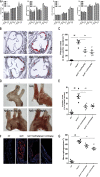
Methods and results: Iso showed significant inhibitory effects on ox-LDL-induced THP-1-derived macrophage injuries via decreasing reactive oxygen species levels, lipid deposition, and caspase-3 activation, restoring mitochondrial membrane potential, reducing the number of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells, and regulating apoptosis-related proteins. We also determined the protective effects of Iso by PI3K/AKT activation and HO-1 induction. Iso reduced the atherosclerotic plaque size in vivo in ApoE-/- mice as assessed by oil red O, Sudan IV staining, and CD68-positive cells, and reduced macrophage apoptosis as assessed by caspase-3 and TUNEL assays in lesions.
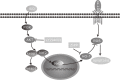
Conclusion: In conclusion, our results show that Iso inhibited atherosclerotic plaque development in ApoE-/- mice by PI3K/AKT activation and HO-1 induction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
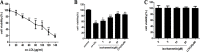


Similar articles
-
Quercetin attenuates high fructose feeding-induced atherosclerosis by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via ROS-regulated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jan;85:658-671. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.077. Epub 2016 Dec 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 27919735
-
Non-Lethal Sonodynamic Therapy Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression in ApoE-/- Mice and Attenuates ox-LDL-mediated Macrophage Impairment by Inducing Heme Oxygenase-1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(6):2432-2446. doi: 10.1159/000475913. Epub 2017 May 3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28468003
-
Lunasin attenuates oxidant-induced endothelial injury and inhibits atherosclerotic plaque progression in ApoE-/- mice by up-regulating heme oxygenase-1 via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/ARE pathway.FASEB J. 2019 Apr;33(4):4836-4850. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802251R. Epub 2019 Jan 2. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30601695
-
Akt Signaling in Macrophage Polarization, Survival, and Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 1;20(11):2703. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112703. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31159424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Isorhamnetin Treatment of Malignant Tumors: Mechanisms and Applications.Nutrients. 2025 May 29;17(11):1853. doi: 10.3390/nu17111853. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulations of the mTORC2-GATA3 axis by an isorhamnetin activated endosomal-lysosomal system of the J774.1 macrophage-like cell line.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2024 Jul;75(1):24-32. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.24-22. Epub 2024 Mar 20. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39070537 Free PMC article.
-
AKT-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of Panax ginseng calyx ethanolic extract.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Oct;42(4):496-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 23. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 30337810 Free PMC article.
-
Isorhamnetin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Activation in Human Bladder Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 4;11(10):1494. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101494. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31590241 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in Familial Hypercholesterolemia, Theranostic Applications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 23;10:894800. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.894800. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35813199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Modulation of Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Axis by Carthamus tinctorius L. Alleviates Vascular Inflammation in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;10(12):2795. doi: 10.3390/plants10122795. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34961267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kriszbacher I, Koppan M, Bodis J. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;353: 429–430. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto A, Naito M, Itakura H, Ikemoto S, Asaoka H, Hayakawa I, et al. Human macrophage scavenger receptors: primary structure, expression, and localization in atherosclerotic lesions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1990;87: 9133–9137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fischer B, von Knethen A, Brune B. Dualism of oxidized lipoproteins in provoking and attenuating the oxidative burst in macrophages: role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. J Immunol. 2002;168: 2828–2834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

